& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
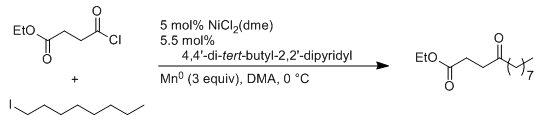
- Negishi coupling: C-C bond formation involving organohalides and organozinc reagents

- Reactant-1 (Nucleophile): Organozinc reagent
- Reactant-2 (Electrophile): Organohalide
- Solvents: THF,
- Catalyst: Catalytic Palladium or Nickel
- Ligand: PPh3, dppe, dppp, dppb, dppf, etc.
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
- Negishi Coupling (SynArchive) – Excellent compilation of reaction schemes with references
Mechanism
Negishi Coupling – General Mechanism (Pd catalyzed)
- The mechanism follows Oxidative addition – Reductive elimination cycle.

Negishi Coupling – General Mechanism (Ni catalyzed)

Ref: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8141; J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 3680
Negishi Coupling – Mechanism with specific example
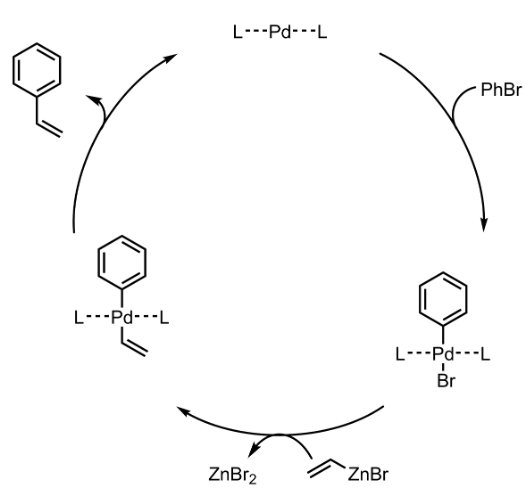
Additional details

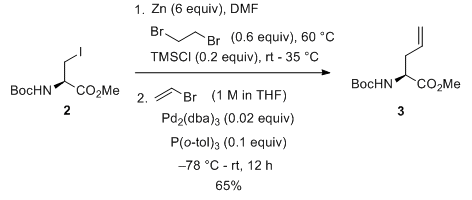
General Procedure:
Note:
- The major advantages of Negishi coupling is high reactivity, high regio- and stereoselectivity, few side reactions and little toxicity.
- Organozincs (for Negishi coupling) are more reactive than organoboranes (for Suzuki coupling) and organostannanes (for Stille coupling).
- Organozinc reagents are generally unstable towards moisture and air. Hence, most of organozinc reagents are not commercially available and are to be generated.
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
- Negishi Coupling-1 (OrgSyn) — Open access
- Negishi Coupling-2 (OrgSyn) — Open access
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
WO2007121484, page no. 174 (to be changed)
Green Chem
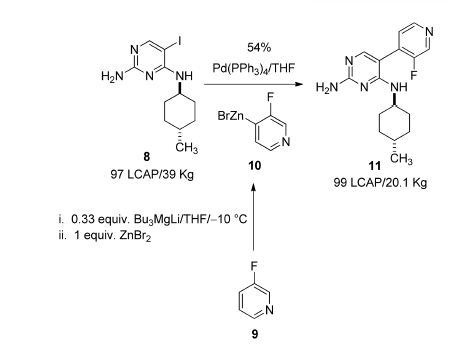
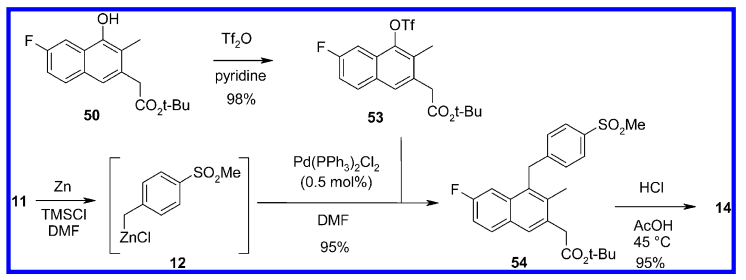
Negishi coupling has been carried out on large-scale.
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
- Multi-Kilo Delivery of AMG 925 Featuring a Buchwald–Hartwig Amination and Processing with Insoluble Synthetic Intermediates (OPRD, 2015) – (a) Organozinc syn; 32.9 Kg of 3-Fluoropyridine, 76.5 Kg ZnBr2, (b) Negishi coupling: 39 Kg batch (Iodo derivative), Pd(PPh3)4 (5 Kg) are used.
- An Efficient Large-Scale Synthesis of a Naphthylacetic Acid CRTH2 Receptor Antagonist (OPRD, 2013) – 500 g batch is reported
Green Chemistry Aspects: