& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
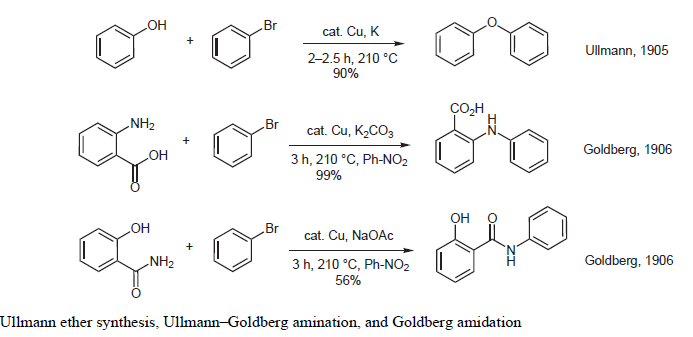
- Ullmann coupling: Cu-catalyzed reaction to form C-C (Ar-Ar) bond, C-N, C-O and C-S bond formation involving aryl halides and corresponding nucleophile
General Scheme:
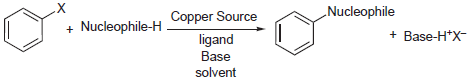
Nu-H = R1R2NH, ArOH, RSH
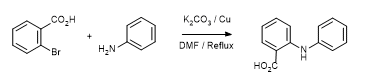
- Reactant-1 (Nucleophile): Aryl halides, Amines, Phenols, thiols
- Reactant-2 (Electrophile): Aryl halides
- Solvents: DMF, DMSO
- Catalyst: Cu metal or Cu salts (e.g: Cu2O)
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
- Ullmann Coupling (SynArchive) – Excellent compilation of reaction schemes with references
Mechanism
Ullmann Coupling – General Mechanism
- The mechanism is not so well defined. However, there are two mechanisms proposed.
- Radical mechanism via SET (Single electron transfer).
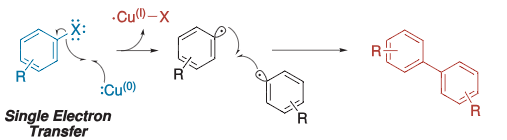
- Oxidative Addition – Reductive elimination cycle
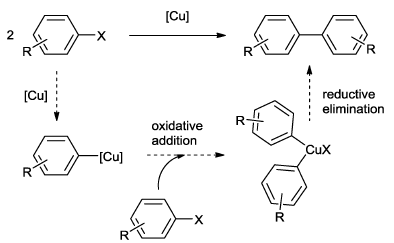
Additional details
General Scheme:

Nu-H = R1R2NH, ArOH, RSH
Cu-Catalyzed Ullmann reactions to form C-N, C-O and C-S bond

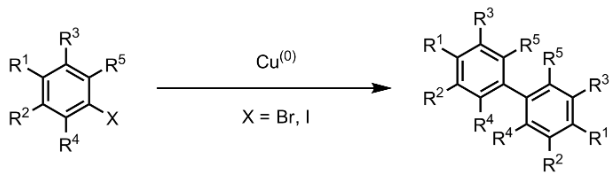
Cu-Catalyzed Ullmann reactions between aryl halides to form biaryls
General Procedure:
The substrate (amine or alcohol; 1 eq.), iodo-aromatic ring (2 eq.), potassium phosphate (4 eq.), N, N’-dimethyl ethylenediamine, and CuI (0.25 equiv.) are suspended in toluene and degassed. The mixture is heated to 100 oC for 12 hours under nitrogen atmosphere. The resulting mixture is filtered and the filtrate is concentrated. The residue is purified by silica column chromatography.
Note:
- Aryl chlorides are usually not reactive and hence not used in Ullmann couplings.
- Aromatic amidation could be done by Ullman condition and it is incompatible with Palladium chemistry
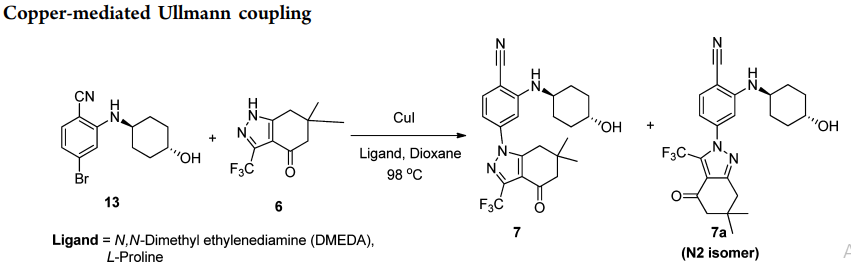
Ullmann and Ullmann-type reactions:
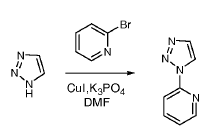
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
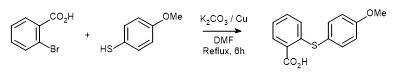
- Coupling of 2-bromobenzoic acid with 4-methoxythiophenol under Ullmann conditions (ChemSpider) — Open access
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
WO2007127635, page no. 245
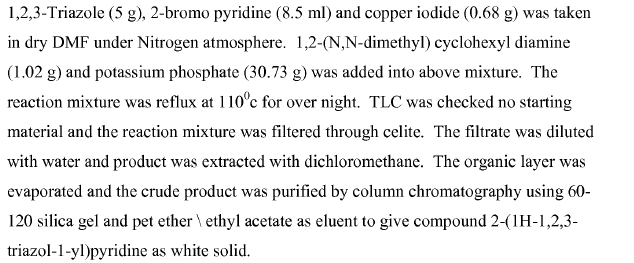
Green Chem
Ullmann coupling and its variants, the most common cross-coupling reaction to form C-N, C-O and C-S bond, have been carried out on large-scale.
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
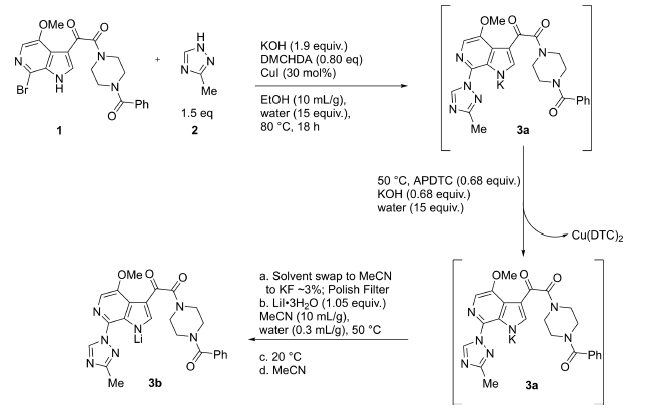
- Process Development and Scale-Up of an Hsp90 Inhibitor (OPRD, 2012) – 13 Kg batch (Bromo derivative), 0.45 CuI and 0.56L ligand (DMEDA) are used
- Preparation of the HIV Attachment Inhibitor BMS-663068. Part 7. Development of a Regioselective Ullmann–Goldberg–Buchwald Reaction (OPRD, 2017) – 158 Kg batch (Br derivative); 19.2 Kg CuI and 38.2 Kg of ligand (DMCHDA, N,N-1,2-dimethylcyclohexanediamine) are used.
Ullmann Coupling & other Ullmann-type reactions – Reviews :