& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
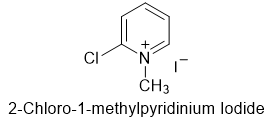
- 2-Chloro-1-methylpyridinium iodide is also called Mukaiyama reagent, a hygroscopic yellow solid
- Mukaiyama reagent is a hygroscopic yellow solid. It is stable and easy to work with.
- The coupling using Mukaiyama reagent is usually performed in DCM, as its by-product is insoluble in DCM and gets precipitated.
- Good results are obtained even for hindered carboxylic acids and alcohols
Mechanism
Acid-Amine coupling by Mukaiyama reagent – Mechanism
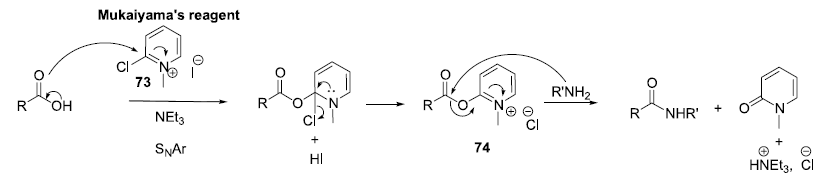
Acid-Amine Coupling by Mukaiyama reagent;

General Procedure:
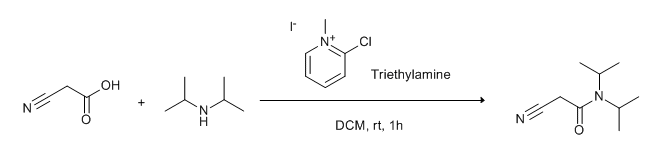
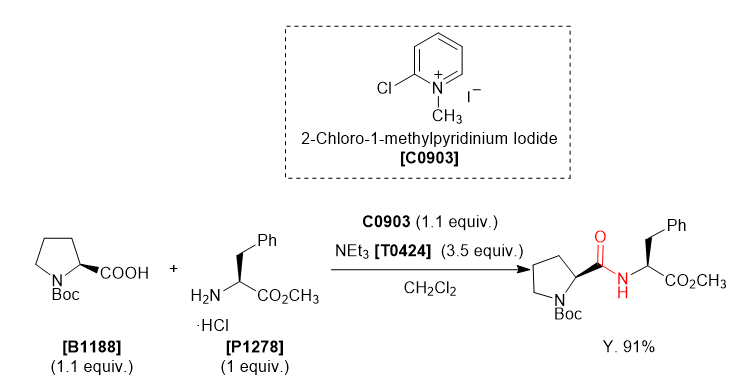
To a solution of acid (1 eq.) in DCM (10 Vol) is added 2-Chloro-1-methylpyridinium iodide (Mukaiyama reagent, 2.5 eq) at 0 °C and stirred for 30 min. To this reaction mixture at 0 °C, amine (1.2 eq.) in DCM (5 Vol) and DIPEA (1.2 eq) are added. The reaction is then brought to RT and stirred overnight. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The organic layer is diluted with CH2Cl2 (10 Vol) and then successively washed with water (15 ml x 2) and brine solution (15 ml). The resultant organic layer is dried using sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- 2-Chloro-1-methylpyridinium iodide is known as Mukaiyama reagent
- The most preferable solvent is DCM.
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
- Amidation of carboxylic acids using 2-Chloro-1-methylpyridinium iodide (Mukaiyama’s reagent) (ChemSpider) — Open access
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
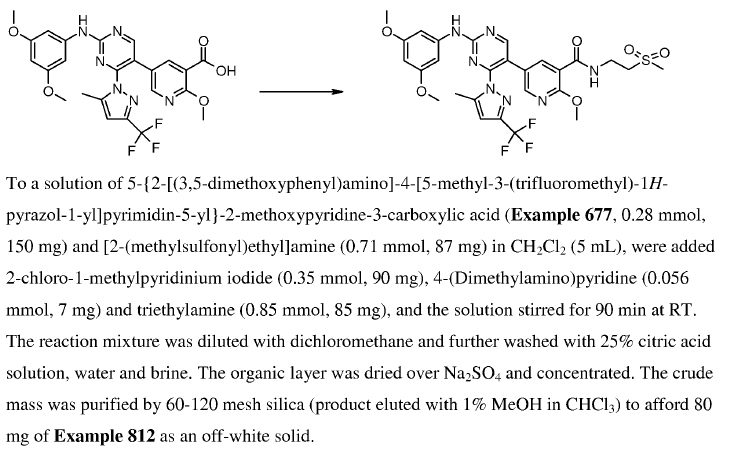
WO2010038081, page No. 680
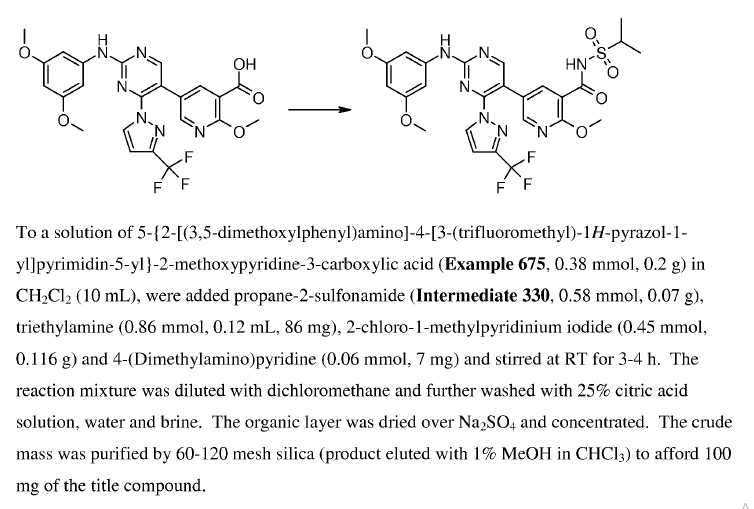
WO2010038081, page No. 687
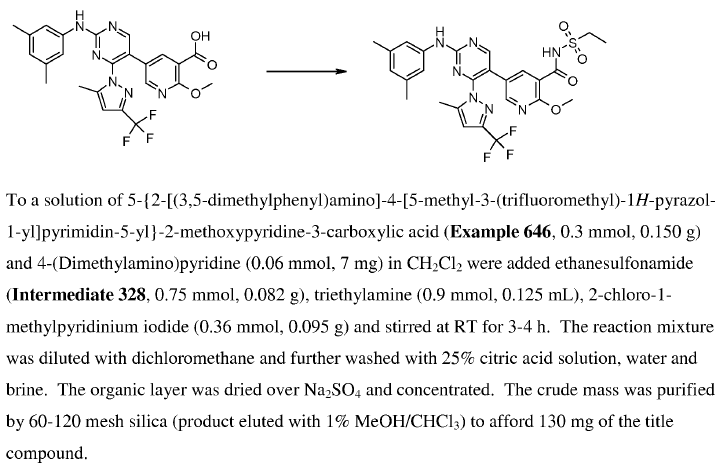
WO2010038081, page No. 694
Green Chem
- Mukaiyama reagent is not generally used in manufacturing