& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
- Sodium borohydride is generally useful for the reduction of aldehydes/ketones to alcohols and imines to amines
- NaBH4 does not reduce other functional groups such as carboxylic acids, nitriles, amides and esters. However, NaBH4 can reduce esters slowly and inefficiently with excess reagent and/or elevated temperatures.
- Sodium borohydride is commercially available as a solid, in powder or pellets, or as a solution in various solvents
- NaBH4 is an excellent source of hydride anion (H– ion)
Comparison of Reducing agents towards carbonyl compounds
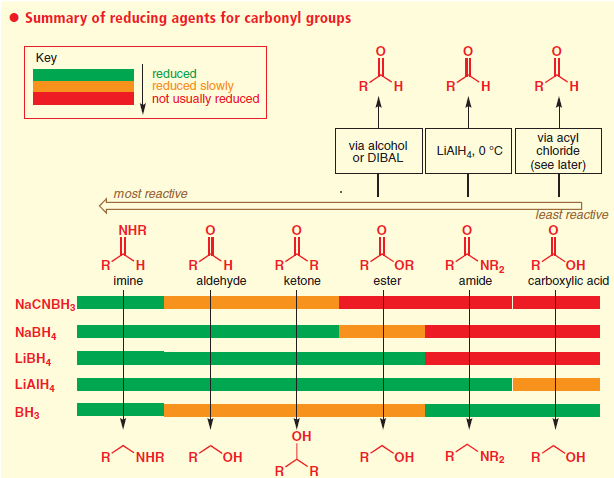
Ref: Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S. Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Oxford UP: Oxford, U.K., 2012; p 534.
Luche Reduction
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
For review papers and other articles,
refer to the tab "References"
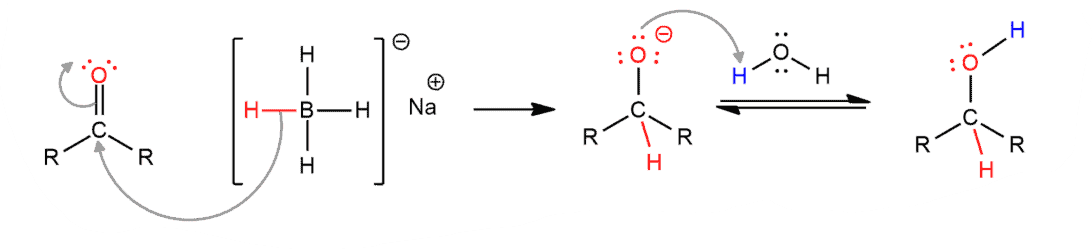
Mechanism
General Reduction Mechanism
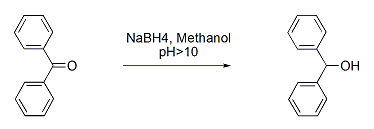
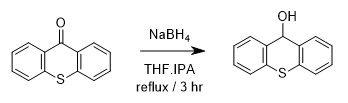
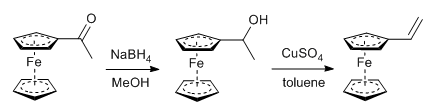
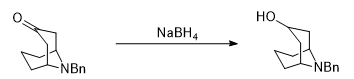
It involves two steps (a) Nucleophilic addition – Hydride ion from NaBH4 attacks carbonyl carbon to alkoxide intermediate (b) Protonation – Alkoxide gets protonated by water or acid during work-up, leading to alcohol
Additional details
NaBH4 Reduction:
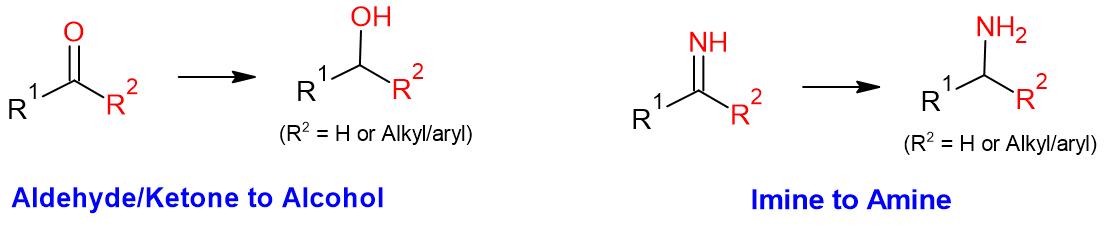
General Procedure:
To a solution of aldehyde/ketone/Imine (1 eq.) in THF (10 Vol) is added NaBH4 (1.2 eq) and striired for 4 h. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The RM is quenched by adding aq. NH4Cl or aq. 1N HCl (10 Vol) at 0 oC and stirred for 2 h. The resultant mixture is extracted with DCM (10 Vol) two times. The combined organic layer is washed with water and brine solution (5 Vol), dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated to afford the desired compound
Note:
- The most preferable solvent is THF, MeOH or EtOH (or mixture of solvents)
- It is usually performed at room temp. or at low temp (0o C), depending on the nature of the reaction
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
- Ketone reduction to 2o alcohol by NaBH4 (OrgSyn) — Open access
- Aldehyde reduction to 1o alcohol by NaBH4 (OrgSyn) — Open access
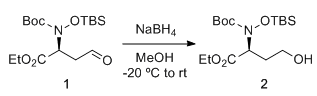
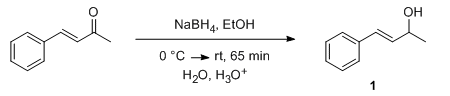
- Enone reduction to Enol by NaBH4 (OrgSyn) — Open access
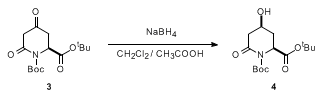
- Selective reduction of Ketone by NaBH4 (OrgSyn) — Open access
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
Patent references
Green Chem
Sodium borohydride has been used on large-scale and there are several reports available in OPRD. NaBH4 is an inexpensive reducing agent that can be used on manufacturing.
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
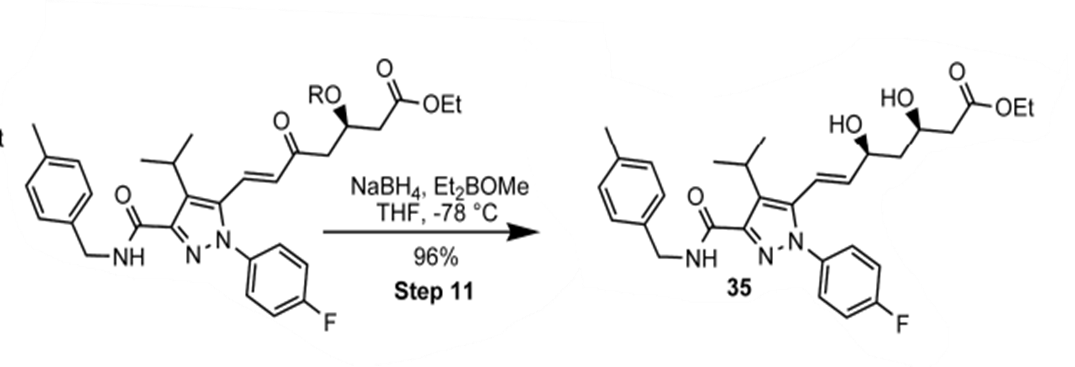
- Development of an Early Enabling Synthesis for PF-03052334-02: A Novel Hepatoselective HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor (OPRD, 2011) – 183 g batch; 444 mL diethylmethoxyborane (1 M solution in THF and 15 g NaBH4 Chiral reduction involving NaBH4 and diethylmethoxyborane
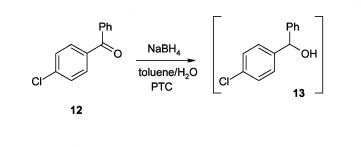
- New Manufacturing Procedure of Cetirizine (OPRD, 2012) – 150 Kg batch (Ketone), 10 Kg NaBH4 and 2.5 Kg methyltrioctylammonium chloride (phase transfer catalyst) are used
Green Chemistry Aspects:
Useful articles for Scale-up: