& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
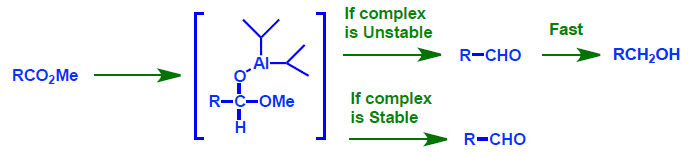
Reaction & Reagents info
- DIBAL-H is also referred to as DIBAL or DIBAH
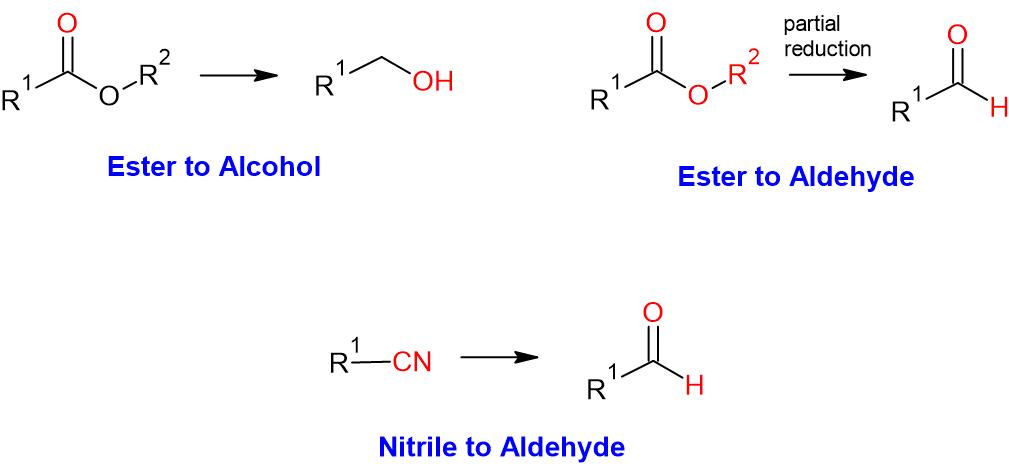
- DIBAL is a strong bulky reducing agent, mainly used for the reduction of ester to primary alcohol and nitrile to aldehydes
- While DIBAL-H reduces esters to primary alcohols, the reaction shall be stopped at aldehyde stage (i.e. partial reduction) if the temperature of the reaction is maintaned at -78 oC
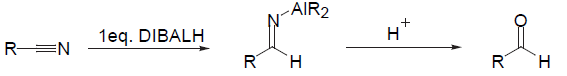
- Nitriles are also reduced to aldehydes. In this case, reaction proceeds via the imine which is hydrolysed on acidic work-up to afford the aldehyde product
- DIBAL is a strong bulky reducing agent, mainly used for the reduction of ester to primary alcohol and nitrile to aldehydes
Other reactions of DIBAL-H
- Lactone can be reduced to Lactol using DIBAL-H
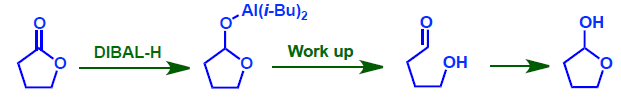
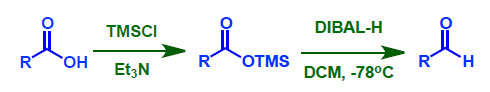
- Acid to Aldehyde: DIBAL-H shall reduce TMS esters to aldehydes
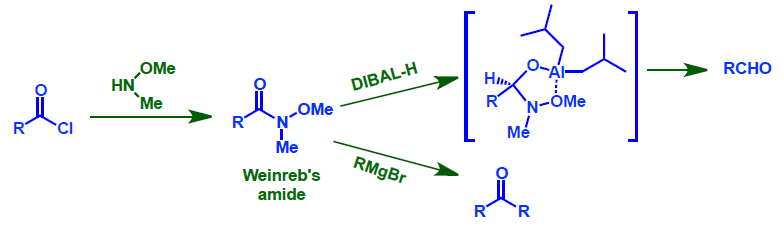
- Weinreb amides can be reduced to aldehyde using DIBAL-H
- Imines are reduced to amines by DIBAL-H
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
- .
For review papers and other articles,
refer to the tab "References"
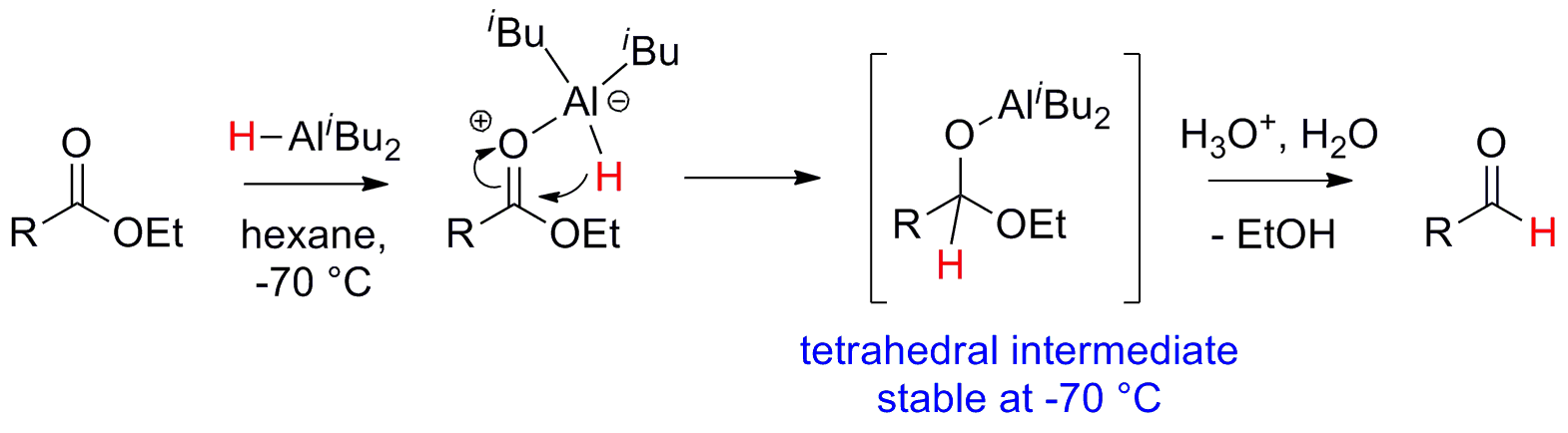
Mechanism
DIBAL-H – Mechanism
Swern Oxidatio
Additional details
General Procedure (Ester to alcohol & Nitrile to Aldehyde):
To a solution of Ester or Nitrile (1 eq.) in DCM or THF or toluene at -78 oC is added DIBAL-H in THF or toluene (1M solution, 1 eq.) dropwise and maintained at -78 oC under nitrogen atmosphere for 2 h. It is slowly brought to room temperature and continued stirring for additional 6 h. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction is quenched by adding methanol slowly, followed by addition of aqueous Rochelle’s salt solution. The resultant suspension is filtered through celite and washed with ethyl acetate/DCM. The layers are separated. The organic layer is then successively washed with water (10 Vol x 2) and brine solution, dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to get the desired compound. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
General Procedure (Ester to aldehyde at -78 oC):
To a solution of Ester (1 eq.) in DCM or THF or toluene at -78 oC is added DIBAL-H in THF or toluene (1M solution, 1 eq.) dropwise and maintained at -78 oC under nitrogen atmosphere for 2 h (It is important to maintain the temp. at or below -78 oC to ensure further reduction does not occur). The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction needs to be maintained at -78 oC throughtout.
The reaction is quenched by adding methanol slowly, followed by addition of aqueous Rochelle’s salt solution. The resultant suspension is filtered through celite and washed with ethyl acetate/DCM. The layers are separated. The organic layer is then successively washed with water (10 Vol x 2) and brine solution, dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to get the desired compound. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
DIBAL shall be quenched by several other methods (Quenching methods of LAH and DIBAL are almost same)
(a) by adding water (1 Vol) , 10 % NaOH (1.5 Vol), and finally again water (3 Vol).
(b) by adding saturated aqueous Na2SO4
(c) by adding aqueous solution of Rochelle’s salt (sodium potassium tartrate, KNaC4H4O6)
Note:
- DIBAL-H reduces (a) esters to alcohols, (b) nitrile to aldehyde and (c) Lactone to Lactol
- If the reaction is maintained at -78 oC, DIBAL-H reduction of ester results in aldehyde (partial reduction). However, it is bit difficult to control DIBAL-H reduction to stop at aldehyde stage
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
Ester to Alcohol using DIBAL:
- Ester reduction (ChemSpider) – Ester to Alcohol — Open access
- Ester to Alcohol-1 (OrgSyn) — Open access
- Ester to Alcohol-2 (OrgSyn) — Open access
Lactone to Lactol using DIBAL:
- Reduction of chroman-2-ones to lactols using diisobutylaluminium hydride (ChemSpider) – Lactone to Lactol — Open access
- Lactone to Lactol-1 (OrgSyn) — Open access
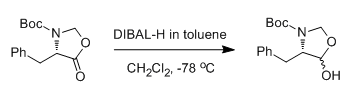
Ester to Aldehyde (partial reduction) using DIBAL:
- Dibal reduction of an amino acid derived methyl ester (ChemSpider) -Ester to Aldehyde (partial reduction at low temp.) — Open access

For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
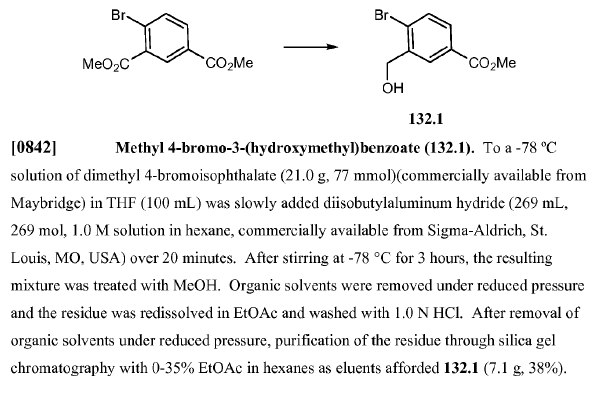
WO2010045258, page No. 349
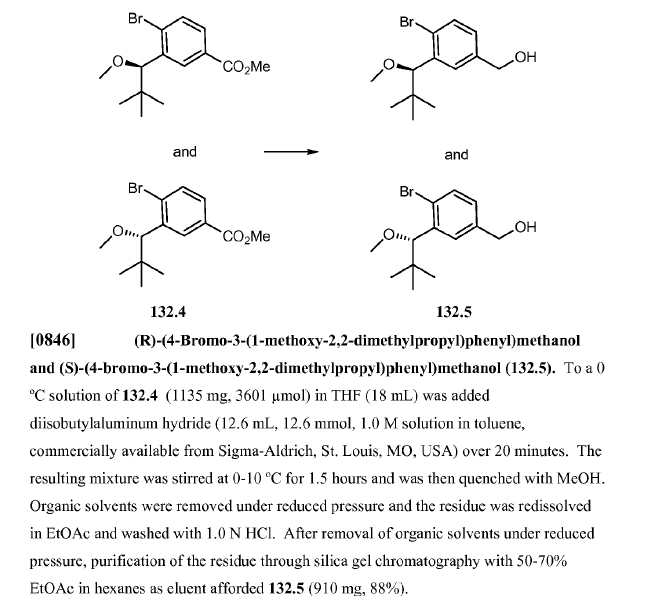

WO2010038081, page No. 818
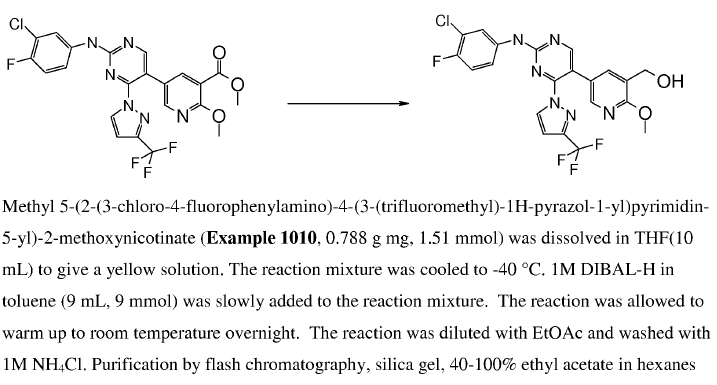
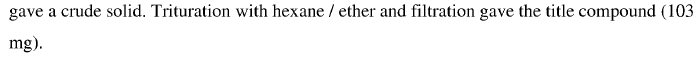
WO2010045258, page No. 347
Green Chem
DIBAL-H reactions have been carried out on large-scale and there are several reports available in OPRD
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
- A Practical and Scalable Method for Manufacturing JAK Inhibitor ASP3627 (OPRD, 2019) – 69 Kg batch; 300 Kg of DIBAL-H (17% in toluene) – A detailed account on reaction optimization has been provided; Nitrile to Aldehyde
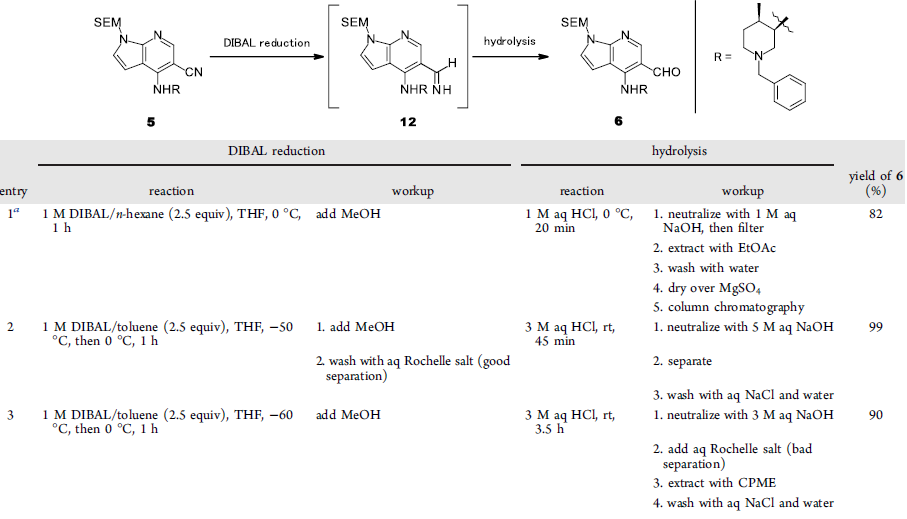
- Multikilogram Synthesis of a Potent Dual Bcl-2/Bcl-xL Antagonist. 2. Manufacture of the 1,3-Diamine Moiety and Improvement of the Final Coupling Reaction (OPR, 2020) – Ketone to Oxime and then Oxime to Amine. For Oxime reduction to Amine, the batch size is 8 Kg (Ketone) and 67.7 Kg of DIBAL-H (1.7M solution in toluene)
Green Chemistry Aspects:
Useful articles for Scale-up:







