& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
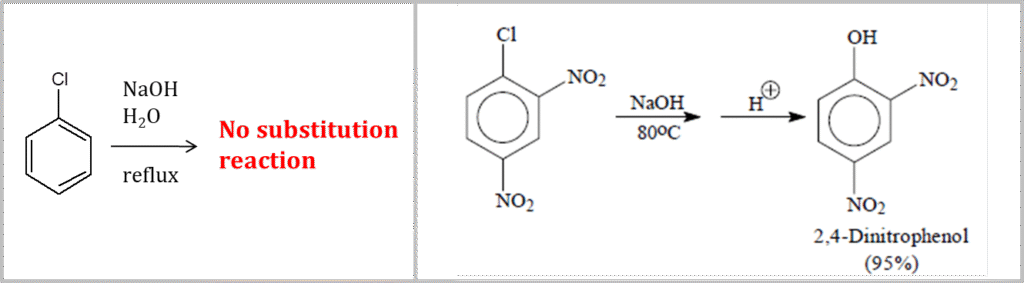
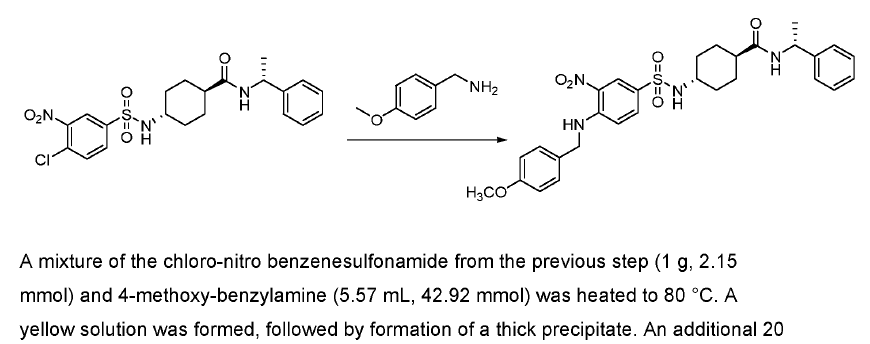
- Normally, electrophilic aromatic substitutions are common with benzene derivative.
- Aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions, as the ring is already electron rich
- Chlorobenzene does not react with NaOH (only under extreme conditions, this reaction occurs). However, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene undergoes reaction with NaOH to result in corresponding Phenol derivative
- Aryl halides do undergo nucleophilic substitution (SNAr) reactions, provided that there are strong electron withdrawing groups are present on the ring

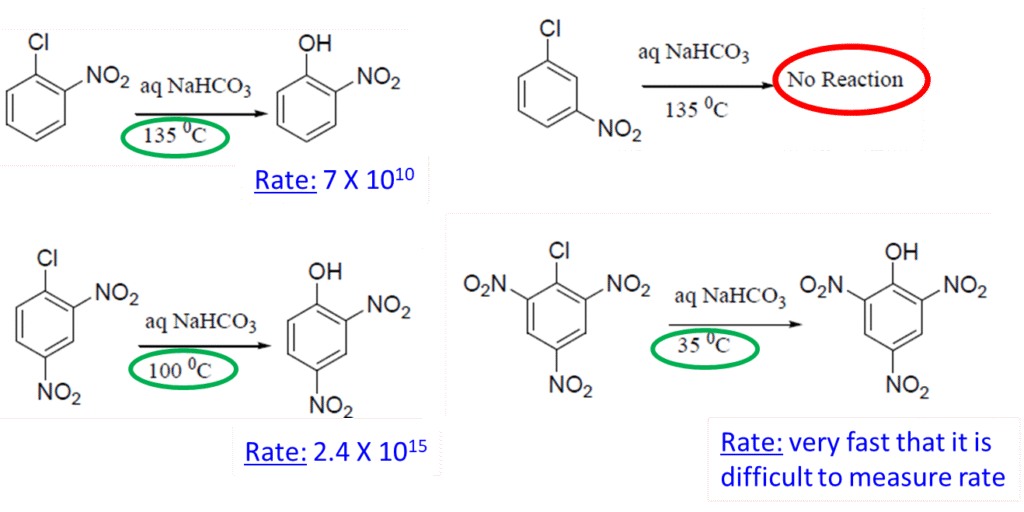
- The reactivity of halogen depends on its electronegativity and ability to act as a leaving group
- The reactivity order in SNAr reactions: F > Cl > Br > I
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
Mechanism
SNAr or Addition-Elimination – Mechanism
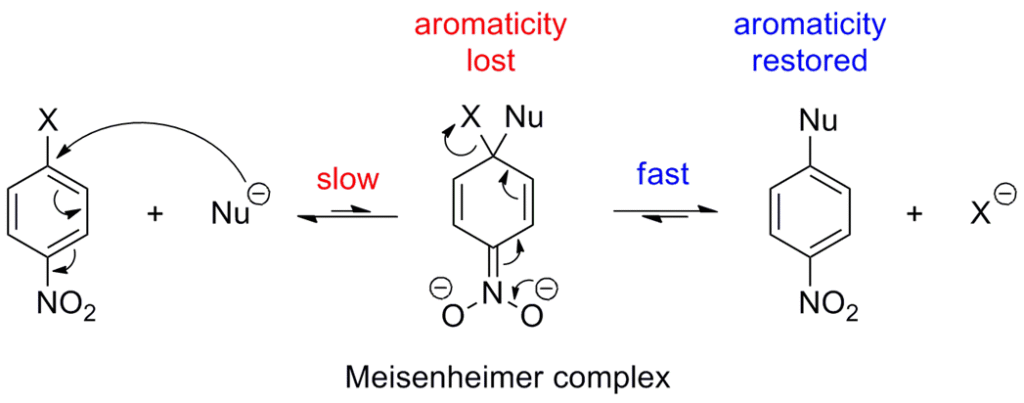
- Step-1: Addition of the nucleophile (:Nu–) to form a carbanion (also called Meisenheimer complex). This is slow rate-determining step
- Step-2: Elimination or loss of leaving group (i.e halide ion) to form the aromatic ring
It is called “Addition-Elimination” mechanism (or) SNAr (Substitution Nucleophilic Aromatic)
Additional details
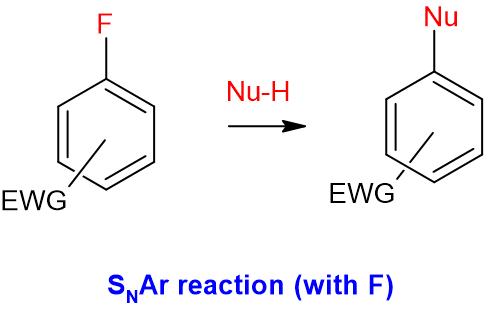
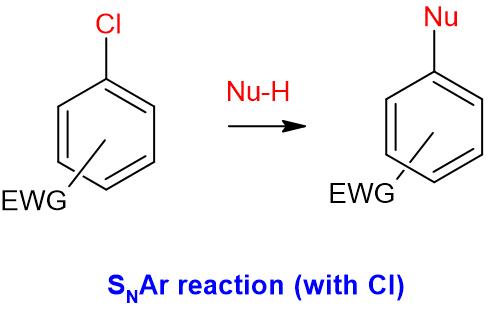
EWG = Electron withdrawing groups such as -NO2, -CN, -SO2R
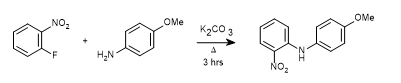
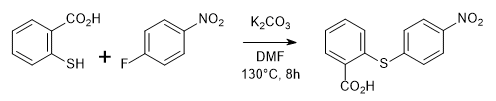
General Procedure-1 (when Nu=amines, thiols and phenols) :
A mixture of Ar-F derivative (1 eq.), Nucleophile (1 eq.), K2CO3 or Cs2CO3 (2 eq.) in acetonitrile or DMF or NMP (10 Vol) is stirred under nitrogen atmosphere at 80 oC for 3 to 4 h. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction mixture is diluted with water (20 Vol) and extracted with DCM or ethyl acetate two times. , The combined organic layer is then successively washed with water (10 Vol) and brine solution, dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to get the desired compound. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
If required, acid-base work-up procedure shall be included for the better isolation
General Procedure-1 (when Nu=aliphatic alcohols) :
To a suspension of NaH (60% dispersion in oil, 1.2 eq.) in THF (10 Vol) at 0 oC is added a solution of Ar-F derivative (1 eq.) in THF dropwise and stirred at room temperature for 6 to 8 h. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction mixture is cooled to 0 oC and quenched by adding isopropanol or methanol or saturated NH4Cl brine solution (to quench excess sodium hydride). Further, the mixture is diluted with water (10 Vol) and extracted with DCM and EtOAc (10 Vol x 2). The combined organic layer is then successively washed with water (10 Vol) and brine solution, dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to get the desired compound. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- Appropriate safety protocols are to be followed while handling NaH
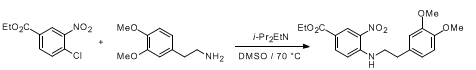
Typical Procedure:
WO2010038081, page No. 284
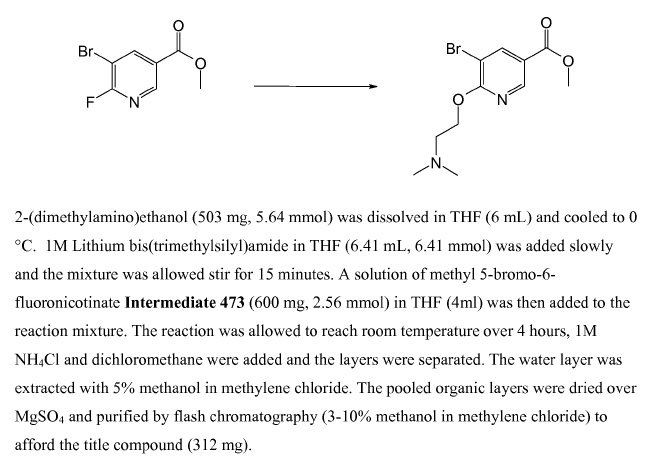

WO2007084786, page No. 132
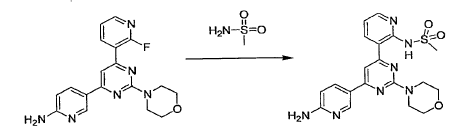

WO2010045258, page No. 341
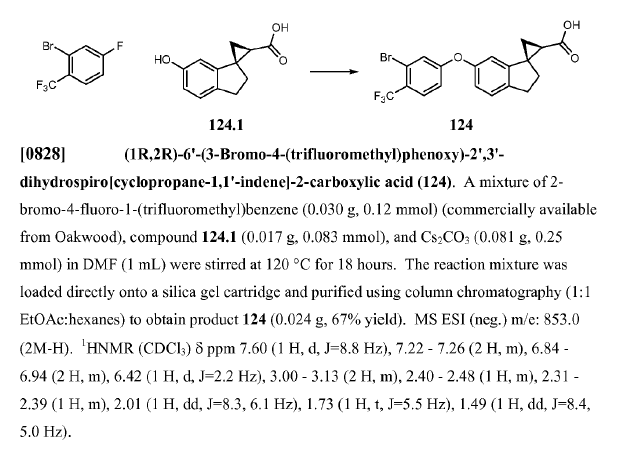
WO2012013716, page No. 100

Green Chem
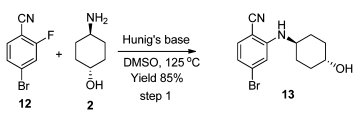
SNAr reactions are commonly carried out on manufacturing scale
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
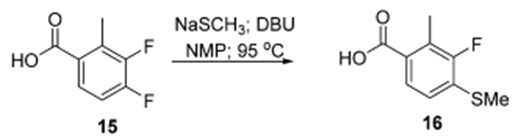
- Process Development and Scale-Up of a Benzoxazepine-Containing Kinase Inhibitor (OPRD, 2015) – 3.85 Kg batch; 3.3 Kg NaSMe and 6.9 L DBU are used
- Process Development and Scale-Up of an Hsp90 Inhibitor(OPRD, 2012) – 1.1 Kg batch (Nitrile derivative)
Green Chemistry Aspects: