& Mechanism
Green Chem.
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
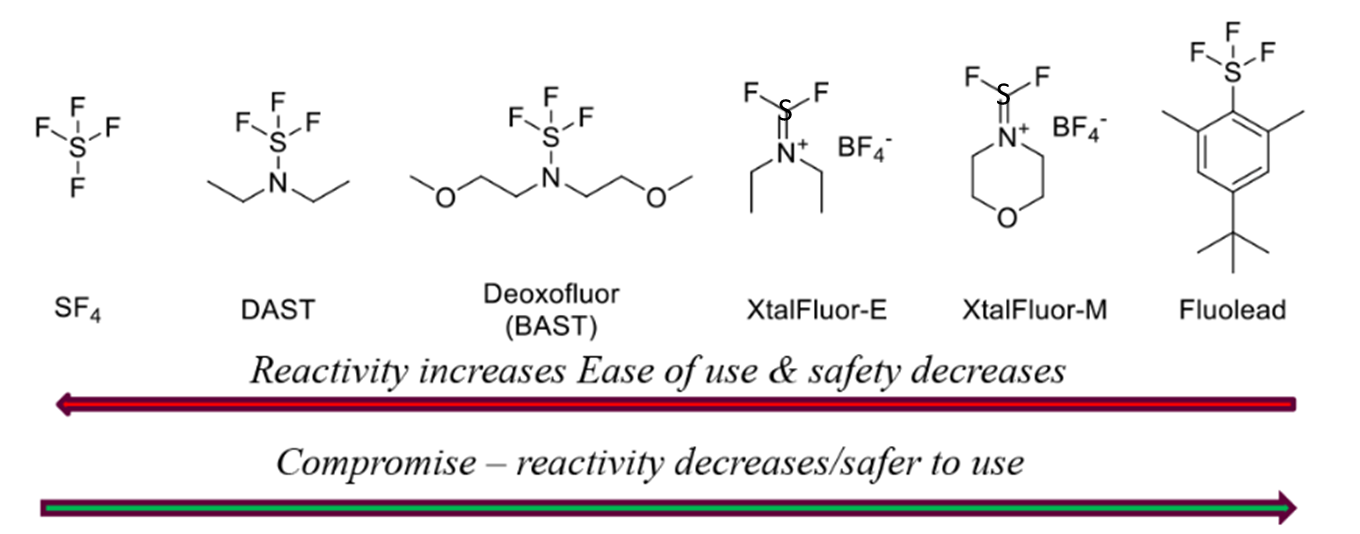
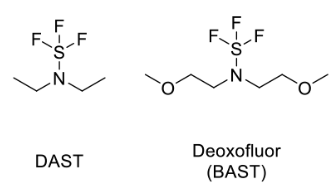
Deoxofluor or BAST [N,N-Bis(2-methoxyethyl)aminosulfur trifluoride]:
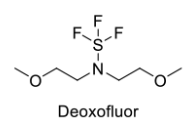
- Deoxofluor or BAST [N,N-bis(2-methoxyethyl)aminosulfur trifluoride], is a nucleophilic fluorinating agent, similar to DAST
- However, Deoxofluor is more thermally stable than DAST and also results in higher yields.
- Deoxofluor or BAST, (N,N-bis(2-methoxyethyl)aminosulfur trifluoride, is a nucleophilic fluorinating agent, similar to DAST
- Deoxofluor reacts with water violently, releasing highly corrosive HF gas. Hence, all operations of Deoxofluor is to be handled in dry atmosphere, with appropriate PPE
Advantages:
- It is more thermally stable and hence large-scale reactions could be performed and reported in literature
Disadvantages:
- Deoxofluor reacts with water violently, releasing highly corrosive HF gas.
- Deoxofluor is required in excess amounts (usually 3 eq. is used)
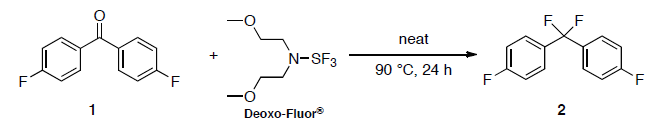
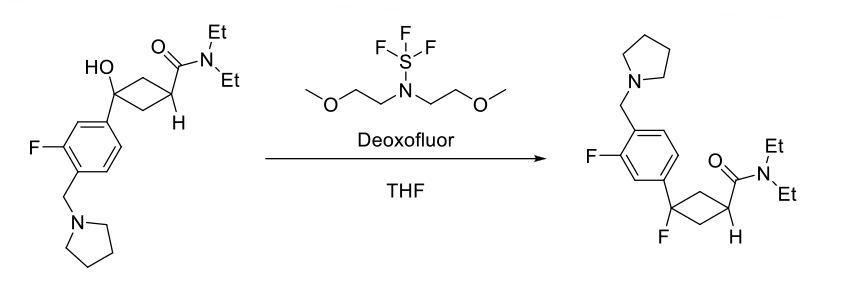
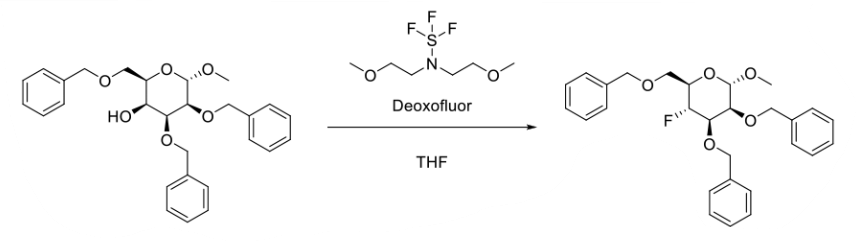
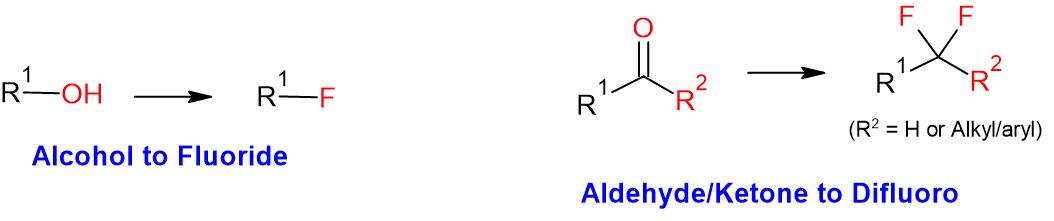
Deoxofluor or BAST – Functional Group Conversions
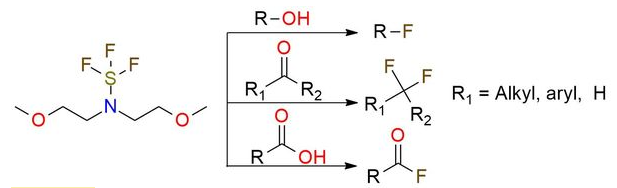
Sulfur-based Deoxyfluorinating reagents
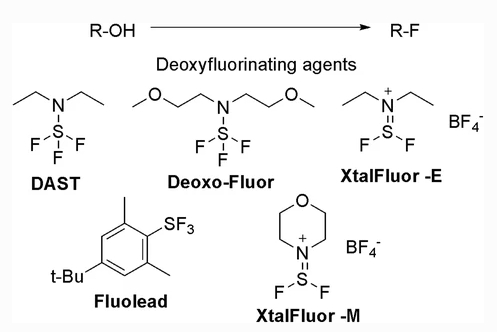
- Stable Fluorinating Reagent with Ease of Handling (FLUOLEAD®) – A safer substitute for DAST
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
- Sulfur-Based Fluorinating Agents (Reagent Guide, ACS Green Chemistry Institute) – Green Chemistry info.
For review papers and other articles,
refer to the tab "References"
Mechanism
Deoxofluor – Mechanism
- The mechanism of Deoxofluor is same as that of DAST

Additional details
General Procedure:
To a solution of alcohol or carbonyl compound (1 eq.) in anhydrous dichloromethane (20 Vol) is added Deoxofluor (3 eq.) dropwise at –0 oC under nitrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for overnight. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction mxture is quenched with saturated solution of NaHCO3 and extracted with dichloromethane two times. The combined organic layer is successively washed with water (10 Vol x 2) and brine solution (5 Vol), dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- The most preferable solvent is DCM. The addition of Deoxo is usually done at 0 oC and the reaction continued at RT.
- Deoxofluor or BAST, (N,N-bis(2-methoxyethyl)aminosulfur trifluoride, is a nucleophilic fluorinating agent,
- Deoxofluor is more thermally stable fluorinating agent, unlike DAST
- Deoxofluor reacts with water violently, releasing highly corrosive HF gas. Hence, all operations of Deoxofluor is to be handled in dry atmosphere, with appropriate PPE
Safer alternative to Deoxofluor:
- Stable Fluorinating Reagent with Ease of Handling (FLUOLEAD®) – A safer substitute for DAST
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
- Process Development of Selectively Benzoylated and Fluorinated Glycosyl Donors (OPRD, 2012) – 35 g batch
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
Patent references
Green Chem.
Deoxofluor has been used on large scale reactions and several OPRD articles have been reported
- Deoxy-Fluor or BAST recations have been performed in Hastelloy C 276 equipment, as HF is generated during the reaction (Ref: OPRD, 2010, 14, 623–631)
Safer alternatives to Deoxofluor:
- Stable Fluorinating Reagent with Ease of Handling (FLUOLEAD®) – A safer substitute for DAST
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
- Process Development of Selectively Benzoylated and Fluorinated Glycosyl Donors (OPRD, 2010) – 83 Kg batch; 37.4 Kg Deoxo-Fluor or BAST is used. The batch was carried out in Hastelloy C 276 reactor
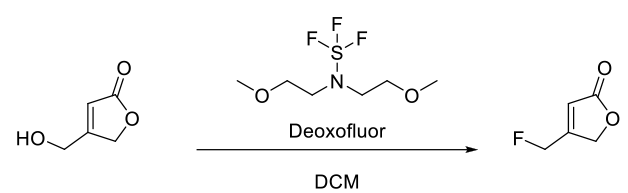
- Development of a Scalable Synthesis of (S)-3-Fluoromethyl-γ-butyrolactone, Building Block for Carmegliptin’s Lactam Moiety (OPRD, 2011) – 10.35 Kg batch (alcohol derivative); 23.54 Kg Deoxo-Fluor or BAST is used.
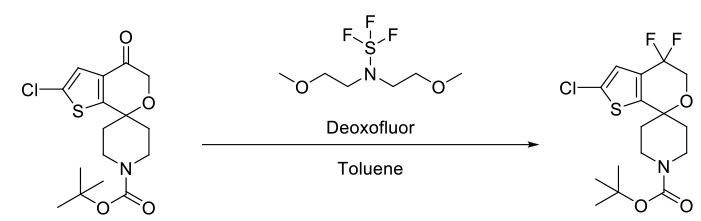
- Synthesis of an ORL-1 Receptor Antagonist via a Radical Bromination and Deoxyfluorination to Afford a gem-Difluorospirocycle (OPRD, 2015) – 15 Kg batch (Ketone derivative); 23.9 Kg Deoxo-Fluor or BAST is used.
Green Chemistry Aspects:
Deoxofluor – References:
- Bis(2-methoxyethyl)aminosulfurTrifluoride: A New Broad-Spectrum Deoxofluorinating Agent with Enhanced Thermal Stability. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 7048–7054.
General Fluorination – References: