& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info

- HBTU is Hexafluorophosphate Benzotriazole Tetramethyl Uronium
- Uronium salts are useful for the coupling of sterically hindered amino acids in peptide synthesis
- When the carboxylic acid contains epimerizable α-stereocenter, 1 eq. of HOBt or HOAt shall be used to suppress epimerization.
Disadvantages of Uronium salts:
- The by-product from these uronium salts, namely N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylurea are cytotoxic
- The presence of high energy moiety (Benzotriazole) makes it less attractive for large-scale reactions – Mild reaction conditions should only be maintained
- As the molecular weight is high, quantities required would be higher, thereby higher cost per mole
Owing to the above reasons, HBTU is not the preferable reagent for process development and only few OPRD reports are available. However, HBTU is widely used for solid-phase peptide synthesis
Comparison of HATU, HBTU and TBTU from Scale-up perspective: Refer to the tab “Scale-up & Green Chem”
Commonly used Uronium salts:
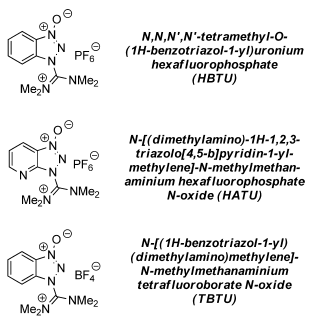
- The counterion in the above salts has no influence on the reactivity
Side-product formation while using HBTU or HATU:
- Uronium species are also known to be guanidylation agents as well

- The side-product formation shall can be diminished by adding HOBt to the reaction (similar to HOBt in DCC)


- HOBt and HOAt have explosive character, especially in water-free form
- HOBt and HOSu are commonly used additives. HOAt is very expensive
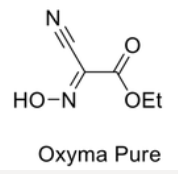
Oxyma Pure® (Ethyl 2-cyano-2-(hydroximino)acetate)
- A recently developed additive and is trademark of Luxembourg Bio Technologies Ltd, Rechovot, Israel
- Oxyma Pure®is a non-explosive alternative to HOBt or HOAt, and allows high coupling rates at low racemization when applied in combination with carbodiimides.
Mechanism
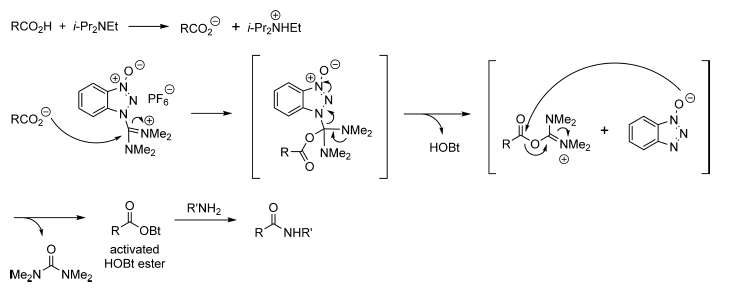
Acid-Amine coupling by HBTU – Mechanism
- The first step is the formation of carboxylate anion with bases such as Et3N or DIPEA
- The next step is the formation of activated HOBt ester by the reaction between carboxylate anion and HBTU. The by-product of HBTU viz., N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylurea is liberated here.
- HOBt ester gets attached by amine to give amide
Additional details
Acid-Amine Coupling by HBTU;

General Procedure:
To a suspension of acid (1 eq.), amine (1.1 eq.) and DIPEA (3.5 eq.) in DMF (10 Vol) was added HBTU (1.5 eq.) and the mixture stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction mixture is diluted with EtOAc or CH2Cl2 (10 Vol) and then successively washed with 10 % citric acid (5 Vol), saturated NaHCO3 solution (5 Vol), water (5 Vol x 2) and brine solution (5 Vol). The resultant organic layer is dried using sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- HBTU is O-(Benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
- The reaction solvents are DMF, DMSO, 2-MeTHF
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
- Condensation Reaction Using HBTU (TCI) — refer to sub-section “Applications & Literature” — Open access
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
Patent references
Green Chem
- Though HBTU is not used widely in process chemistry, HATU and TBTU are used for process development.
- Both HATU and TBTU provide faster couplings, reduce epimerization and result in high yields (Ref: OPRD, 2016, 140-177)
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
- Large-Scale Applications of Amide Coupling Reagents for the Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals (OPRD, 2016) – Excellent review article, providing comprehensive information on large-scale reactions of coupling reagents


