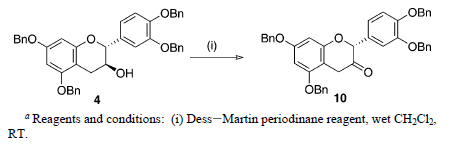
Reaction & Reagents info
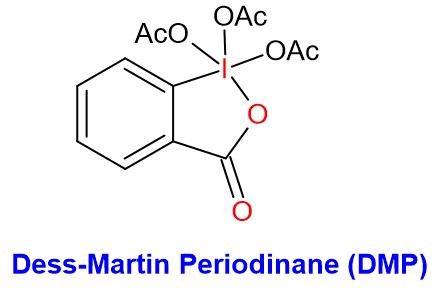
- Dess-Martin periodinane (DMP) is a mild oxidizing agent that converts primary alcohol to aldehyde and secondary alcohol to ketone
- DMP is very similar to IBX in reactivity. The presence of acetate groups makes DMP more soluble in a wider range of solvents compared to the IBX reagent
Advantages
- The reagent, being mild, the reaction shall be performed under room temp. and neutral pH. Hence, it shows high chemoselectivity and tolerance towards most functional groups.
- The reaction is usually shorter duration, involves simple work-ups and results in high yields.
- Also, it is less toxic, compared to chromium-based alternatives (PCC and PDC)
Disadvantages
- DMP is shock sensitive and potential explosive
- It is quite expensive
- Being higher molecular weight, quite a lot of material is to be used. Atom efficacy is poor from Green Chemistry’s perspective
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
- Dess-Martin Periodate (DMP) (Reagent Guide, ACS Green Chemistry Institute) – Green Chemistry info.
- Dess-Martin Oxidation (SynArchive) – Excellent compilation of reaction schemes with references
Mechanism
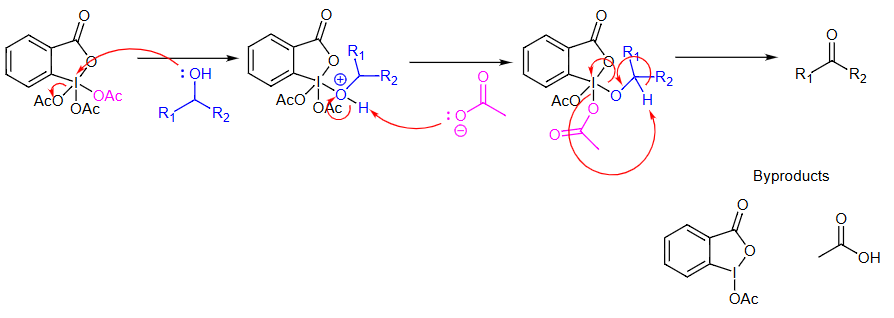
Additional details
Acid-Amine Coupling using NHS ester route;

General Procedure:
To A stirred, cooled solution of acid (1 eq.) at 0 oC in DCM (10 Vol) at 0 oC is treated dropwise with N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS, 1 eq.) and DCC or EDCI (1 eq.) and stirred at 0 oC for one hour. A solution of amine (1.2 eq.) in DCM (60 ml) is added at 0 oC and stirred at room temperature for 2 h. The reaction is then brought to RT and stirred overnight. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The organic layer is diluted with CH2Cl2 (10 Vol) and then successively washed with water (15 ml x 2) and brine solution (15 ml). The resultant organic layer is dried using sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- NHS (N-Hydroxysuccinimide) acts as an activating agent for -COOH, making it active ester for coupling reaction
- DCC is Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and EDCI is 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (also mentioned as EDC, EDAC)
- The most preferable solvent is DCM or EtOAc. Other solvents are DMF
- DCC (Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide), wherein the by-product (Dicyclohexylurea) is insoluble requires filtration. However, the byproduct from EDCI namely 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)urea is soluble in water. Hence, the work-up becomes much easier in case of EDCI
Typical Procedure:
WO2010038081, page No 477

DMP is not a suitable oxidizing agent for larger scale reactions owing to following reasons:
- DMP is shock sensitive and potential explosive
- It is quite expensive
- Being higher molecular weight, quite a lot of material is to be used. Atom efficacy is poor from Green Chemistry’s perspective
Only very few examples are available on the use of DMP on bulk scale
- Scale-Up Syntheses of Two Naturally Occurring Procyanidins: (−)-Epicatechin-(4β,8)-(+)-catechin and (−)-Epicatechin-3-O-galloyl-(4β,8)-(−)-epicatechin-3-O-gallate (OPRD, 2007) – 315 g of DMP has been used.
Green Chemistry Aspects: