& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
- In order to avoid racemization and side product formation during coupling, several reagents have been developed wherein “-OBt ester” is generated in-situ. e.g; HBTU, HATU, TBTU, BOP, PyBOP etc..
- Besides amidation, PyBOP is useful for selective esterification and lactonization.
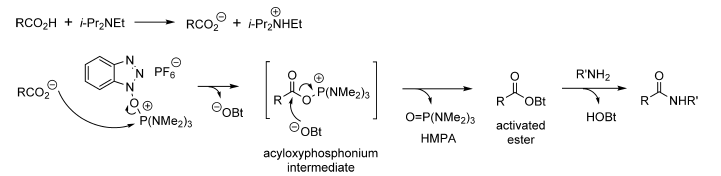
- The first step is the formation of carboxylate anion with bases such as Et3N or DIPEA
- The next step is the formation of activated HOBt ester by the reaction between carboxylate anion and BOP. The by-product of HMPA ((hexamethylphosphoramide) is liberated here.
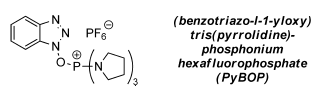
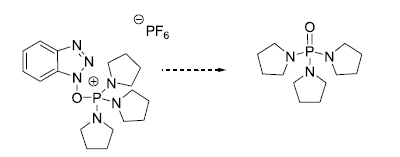
- PyBOP shall be considered as an alternative to BOP, as PyBOP by-product viz., tris(pyrrolidin-1-yl)phosphine oxide, is more benign.
- The major disadvantage in using BOP is that it generates a highly carcinogenic HMPA (hexamethylphosphoramide) as a by-product during coupling reaction
Comparison of BOP and PyBOP from Scale-up perspective: Refer to the tab “Scale-up & Green Chem”
Mechanism
Acid-Amine coupling by PyBOP – Mechanism
- The first step is the formation of carboxylate anion with bases such as Et3N or DIPEA
- The next step is the formation of activated HOBt ester by the reaction between carboxylate anion and BOP. The by-product of HMPA ((hexamethylphosphoramide) is liberated here.
- HOBt ester gets attached by amine to give amide
- The mechanism of PyBOP is same as that of BOP, except that the by-product viz., tris(pyrrolidin-1-yl)phosphine oxide, is released from PyBOP and HMPA from BOP
- The next step is the formation of activated HOBt ester by the reaction between carboxylate anion and PyBOP. The by-product [tris(pyrrolidin-1-yl)phosphine] oxide is liberated here.
Additional details
Acid-Amine Coupling by pyBOP;

General Procedure:
To a solution of acid (1 eq.) amine (1.2 eq.), DIPEA or Et3N (1.5 eq) in DMF (10 Vol) at 0 oC is added PyBOP (1.2 eq.). The reaction is then brought to RT and stirred overnight. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The organic layer is diluted with CH2Cl2 (20 Vol) and then successively washed with 10 % citric acid (10 Vol), water (10 Vol x 2), NaHCO3 solution and brine solution. The resultant organic layer is dried using sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- PyBOP is Benzotriazol-1-yloxytripyrrolidinophosphonium hexafluorophosphate
- The most preferable solvent is DMF.
- The by-product of PyBOP is not a carcinogen and it is an substitute for BOP. However, PyBOP is a potenial explosive
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
Patent references
Green Chem
- PyBOP shall be considered as an alternative to BOP, as PyBOP by-product viz., tris(pyrrolidin-1-yl)phosphine oxide, is more benign.
- However, PyBOP is expensive and it has not been found much use in manufacturing so far (Ref: OPRD, 2016, 140-177)
- Also, PyBOP is a potential explosive