& Mechanism
Green Chem.
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
- Appel reaction involves mild conditions, converting aliphatic alcohols to alkyl chlorides/bromides
- When the alcohol is 1o or 2o, the reaction occurs via SN2, proceeding with inversion of configuration. However, when it is 3o, it proceeds via SN1, leading to racemic mixture
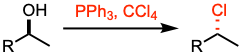
Advantages
- Mild condition to synthesize alkyl halide, unlike acidic SOCl2 condition
Disadvantages
- The by-product namely triphenylphosphine oxide (TPPO) is usually removed by filtration. Sometimes, it is bit difficult to remove residual TPPO, making column chromatography mandatory for the purification
- Use of CCl4 is restricted due to environmental concerns
- CBr4 is hazardous and not environmental friendly
- Also, refer to other reactions involving triphenyl phosphine: Mitsunobu reaction, Suzuki Coupling
Other ways of synthesizing better leaving groups for SN2 reactions:
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
- Appel reaction (SynArchive) – Excellent compilation of reaction schemes with references
For review papers and other articles,
refer to the tab "References"
Mechanism
Mechanism
It involves 4 stages (a) Generation of Phosphonium salt (b) Deprotonation of alcohol, leading to alkoxide species (c) Reaction between alkoxide and (d) SN2 displacement by halide
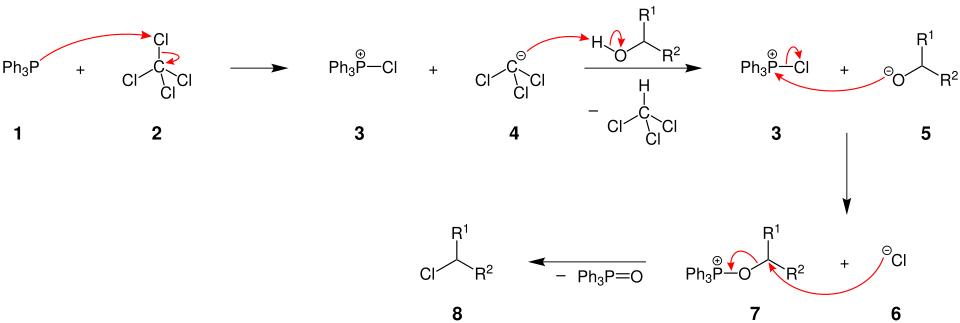
Additional details

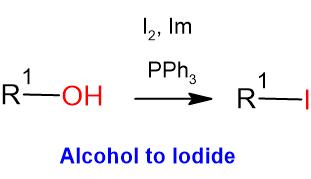
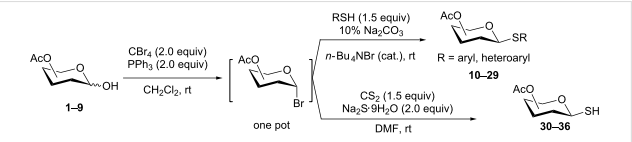
General Procedure-1 (for Chloro and Bromo):
Alcohol (1 eq) and triphenyl phosphine (2 eq.) are taken in dichloromethane (10 Vol) and cooled to 0 oC. CBr4 or CCl4 (2 eq.) in dichloromethane (10 Vol) is added dropwise and the mixture stirred at room temperature. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction mixture is filtered to remove the by-product triphenylphosphine oxide. The filtrate (i.e. organic layer) is successively washed with water (15 ml x 2) and brine solution (15 ml), dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
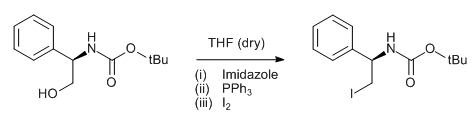
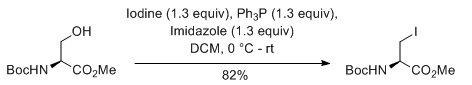
General Procedure-2 (for Iodo):
Alcohol (1 eq) and triphenyl phosphine (2 eq.) are taken in DCM (10 Vol) and cooled to 0 oC. Iodine (2 eq) and Imidazole (3 eq.) in dichloromethane (10 Vol) is added dropwise at 0 oC and the mixture stirred at room temperature. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction mixture is filtered to remove the by-product triphenylphosphine oxide. The filtrate (i.e. organic layer) is successively washed with saturated solution of sodium thiosulphate (10 Vol), water (10 Vol x 2) and brine solution (15 ml), dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- The most preferable solvent is DCM and THF. The reaction is usually performed at RT
- The by-product namely triphenylphosphine oxide (TPPO) is usually removed by filtration
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
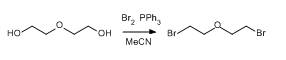
- Bromination of Diethylene Glycol (ChemSpider) — Open access
- Bromination of an alcohol (ChemSpider) — Open access
- Iodination of BOC protected phenylglycinol (ChemSpider) — Open access
- Substitution of hydroxy by iodide in phthalic anhydride protected phenylglycinol (ChemSpider) — Open access
- Alcohol to Iodide-1 (OrgSyn) — Open access
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
WO2010045258, page No. 256
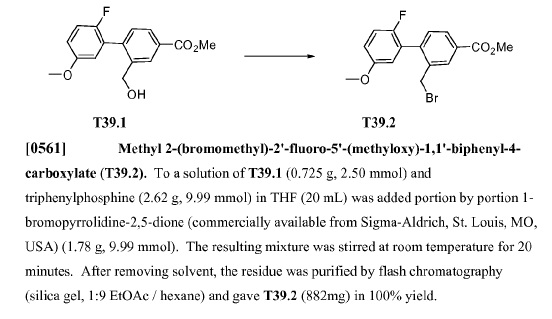
- NBS is also known as 1-Bromopyrrolidine-2,5-dione
Green Chem.
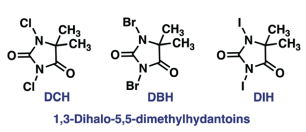
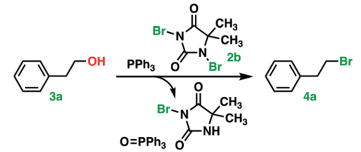
Appel reaction has its own restrictions, as both CCl4 and CBr4 are not environment-friendly. However, environmentally benign reagents are being considered in this context
Environmentally benign Appel reaction:
- An environmentally benign and high-rate Appel type reaction, React. Chem. Eng., 2022, 7, 1650-1659 — Open access
– Dimethyl hydantoin derivatives such as DBH, DCH, DIH have been used as benign reagents
Alternative to Appel reaction for Scale-Up to avoid CCl4:
- Alcohol to Chloride using Oxalyl chloride, (COCl)2
Green Chemistry Aspects: