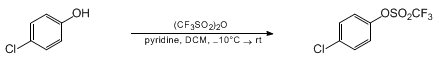& Mechanism
Green Chem.
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
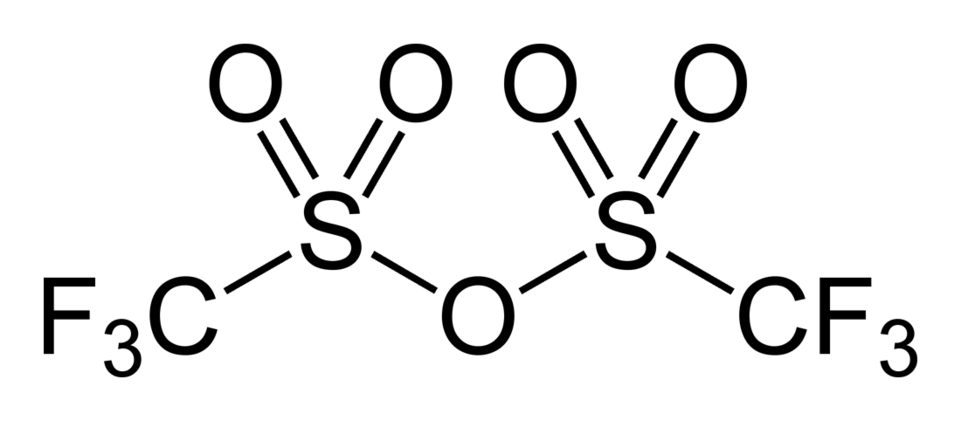
- Trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride is also called Triflic anhydride (Tf2O)
- OH– ion (hydroxide ion), as such, is a poor leaving group, as it is quite strong base. However, OH group shall be converted to a better leaving group such as OMs, OTs or OTf groups for further useful organic conversion
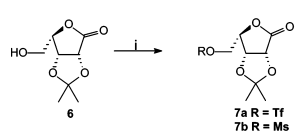
Sulfonates as better leaving groups
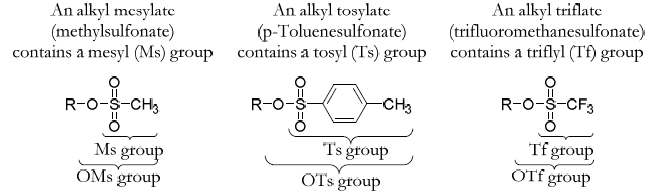
- Leaving group ability; OTf > OTs > OMs
Other ways of synthesizing better leaving groups for SN2 reactions:
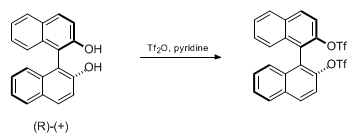
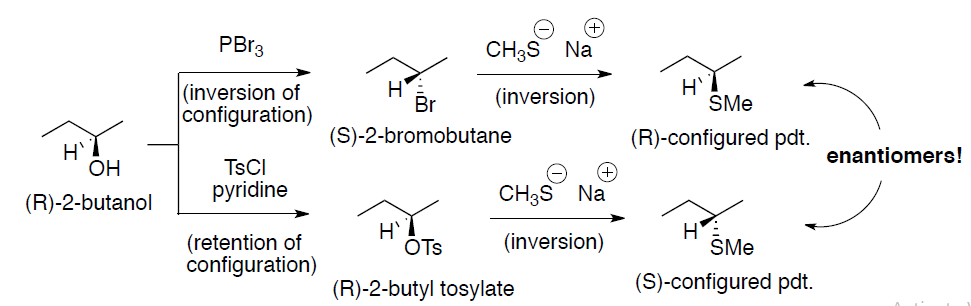
Stereochemical outcome of sulfonate ester (OMs, OTs and OTf):
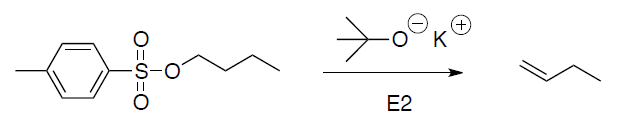
- Alkyl sulfonates undergo SN2 and E2 reaction in a manner identical to that of alkyl halides
(a) Substitution:
(b) Elimination:
For review papers and other articles,
refer to the tab "References"
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
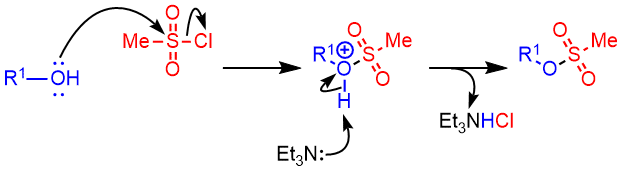
Mechanism
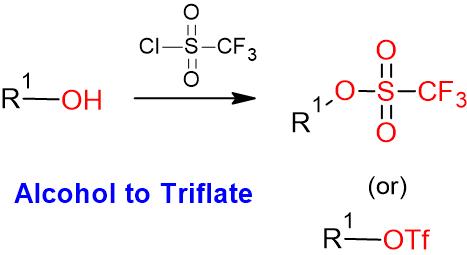
Alcohol to Triflate – Mechanism
The mechansim of triflate formation is same as that of mesylation
Additional details
General Procedure:
To a solution of alcohol (1 eq.) in dry DCM (10 Vol) at 0 oC was added pyridine (1.5 eq.), few drops of DMAP (1.2 eq.) and Trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride (triflic anhydride, 1.2 eq.) and stirred at 0 oC for 4 h (If the reaction does not proceed, it shall be brought to room temperature and stirred for 2 h). The reaction is monitored by TLC. After the completion of the reaction, The organic layer is diluted with CH2Cl2 (10 Vol) and then successively washed with 10 % citric acid (10 Vol), water (10 Vol x 2), NaHCO3 solution and brine solution. The resultant organic layer is dried using sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to get the desired compound.
Note:
- The preferable solvent is DCM. THF shall also be used.
- Common bases are Pyridine, DIPEA, Et3N
Typical Procedure:
- Alcohol to Triflate-1 (OrgSyn) — Open access
- Alcohol to Triflate-2 (OrgSyn) — Open access
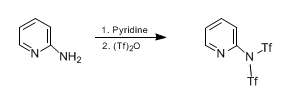
- -NH2 to -NTf2-4 (OrgSyn) – N-Triflates are also synthesized, as similar to O-Triflates — Open access
WO2010045258, page No. 263


Green Chem.
Triflates have been synthesized on large-scale and they are key intermediates in the manufacturing of pharmaceutical intermediates
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
- Multikilogram Synthesis of a Hepatoselective Glucokinase Activator (OPRD,2012) – 119 g batch of 4,4,5,5,5-pentafluoropentanol; 15 Kg batch of alcohol (input); 29.6 Kg of triflic anhydride is used; 25 Kg of triflate is synthesized (output)
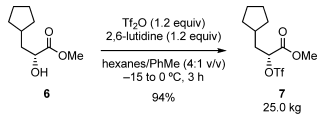
- A Concise, Economical, and Diastereoselective Synthesis of Methyl DGJ Isopropylidene: An Iminocyclitol Molecule Core for Analogue Synthesis (OPRD, 2006) – 500 g batch; 537 mL of trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride (Tf2O) is used.
Green Chemistry Aspects: