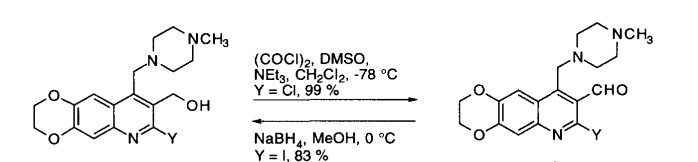
Reaction & Reagents info
- Swern Oxidation (DMSO, Oxalyl chloride) is a mild oxidizing system that converts primary alcohol to aldehyde and secondary alcohol to ketone
- It is one of the series of oxidations involving DMSO (refer to DMSO-activated oxidations)
Advantages
- Inexpensive oxidation method on manufacturing scale
- Also, it is less toxic, compared to chromium-based alternatives (PCC and PDC)
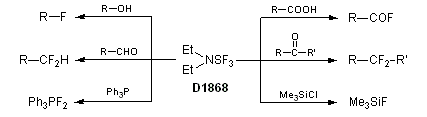
DAST – Functional Group Conversions
Disadvantages
- The liberation of gases viz., malodrous dimethylsulphide (Me2S) and poisonous carbon monoxide (CO) are to be handled appropriately
- It is important to maintain the reaction mixture at -78 oC. If the temperature is not maintained, there is a possibility of formation of mixed thioacetals (see mechanism)
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
- DMSO –Oxalyl Chloride (Swern Oxidation) (Reagent Guide, ACS Green Chemistry Institute) – Green Chemistry info.
- Swern oxidation (SynArchive) – Excellent compilation of reaction schemes with references
Mechanism
General Oxidation Mechanism
DMSO, as such, is not a good oxidising agent. However, it needs to be activated by an activator [such as (COCl)2 in Swern Oxidation, DCC in Moffatt oxidation] so that DMSO shall act effective oxidising agent (refer to DMSO-activated Oxidations)
Activation of DMSO by Oxalyl Chloride
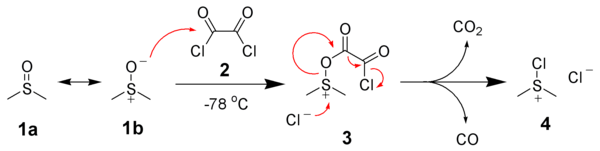
Swern Oxidation

Formation of side product in Swern Oxidation
In Swern oxidation employing (COCl)2, one mole each of CO, CO2 and Me2S (all gaseous products) are released. HCl gets converted to NEt3.HCl during the reaction
It is important to maintain the reaction mixture at -78 oC. If the temperature is not maintained, there is a possibility of formation of mixed thioacetals

Image from “chemistryworld.com”
Additional details

General Procedure:
To a solution of ketone or aldehyde (1 eq.) in dichloromethane (20 Vol) is added DAST (1.2 eq.) dropwise at –78 oC under nitrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 2 h. The reaction is monitored by TLC. The reaction mxture is quenched with saturated solution of NaHCO3 and extracted with dichloromethane two times. The combined organic layer is successively washed with water (10 Vol x 2) and brine solution (5 Vol), dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- The most preferable solvent is DCM and the reaction is usually performed at 0 oC to -78 oC.
- DAST, (Diethylamino)sulfur trifluoride, is a nucleophilic fluorinating agent.
- DAST is heat sensitive and moisture sensitive. In general DAST reactions should not be heated,.
- DAST is useful for dfluorination of carbonyl compounds as well
- Stable Fluorinating Reagent with Ease of Handling (FLUOLEAD®) – A safer substitute for DAST
Typical Procedure:
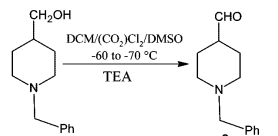
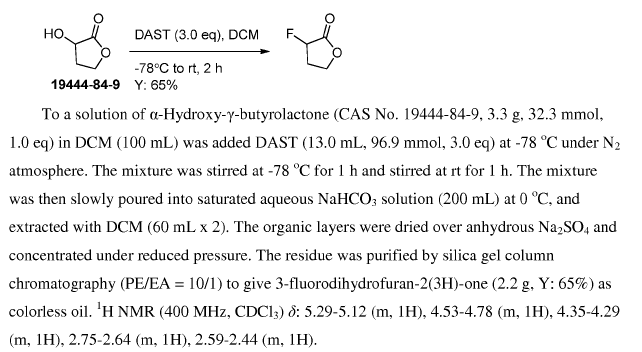
WO2016011390, page No. 382
Swern oxidation could be carried out on large-scale. However, the reaction involves the liberation of 1 eq. each of the gases such as Me2S (dimethylsulphide), CO (carbon monoxide), CO2. Appropriate safety controls are to be ensured while performing manufacturing. During work-up, HCl gets converted to amine salt (such as NEt3.HCl).
- Swern Oxidation is one of the inexpensive methods to manufacture aldehydes or ketones from Alcohols
- The liberation of gases viz., malodrous dimethylsulphide (Me2S), poisonous carbon monoxide (CO) and CO2 are to be handled appropriately
- It is important to maintain the reaction mixture at -78 oC. If the temperature is not maintained, there is a possibility of formation of mixed thioacetals (see mechanism in General Info section)
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
- An Improved and Efficient Process for the Production of Donepezil Hydrochloride (OPRD, 2008) – 4 Kg batch; 3.5 Kg of DMSO & 3.7 Kg of (COCl)2 have been used
- Convergent Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Camptothecin Analog GI147211C (Tetrahedron, 1997) – 100 g batch
Green Chemistry Aspects: