& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
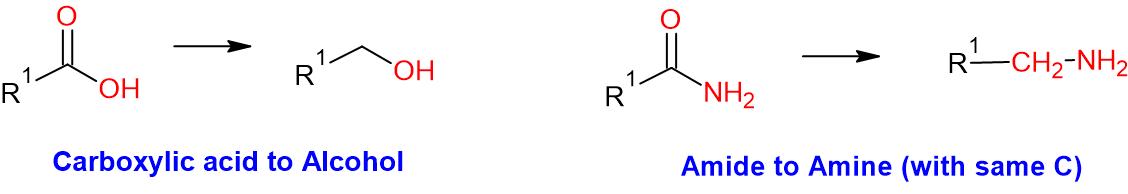
- Borane is generally useful for the reduction of carboxylic acid to primary alcohol and amide to amine. It does not reduce esters and lactone
- BH3 is a reactive gas that exists mostly as a dimer, diborane (B2H6)

- For ease of handling in the laboratory, the reagent is used most often as a commercially available solution of BH3 in THF or BH3 in Me2S
- Borane is a strong Lewis acid that reacts readily with Lewis bases. Borane forms a stable complex with ethers such as THF or thioether

- LAH reacts violently with protic solvents such as alcohol, water (compare with NaBH4, wherein MeOH or EtOH is used as a reaction solvent)
- Borane is a strong Lewis acid that reacts readily with Lewis bases. Hence, Borane forms a stable complex with ethers such as THF or thioethers

- Borane is an electrophile and therefore it attacks the most electrophilic center (Thus, alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reactions with borane). Similarly, between amides and esters, boranes reduces amide.

Ease of Reduction of some Functional Groups with Borane:

Other borane reagents for reduction:
- Several types of boranes have been developed for specific purposes of reduction


Comparison of Reducing agents towards carbonyl compounds
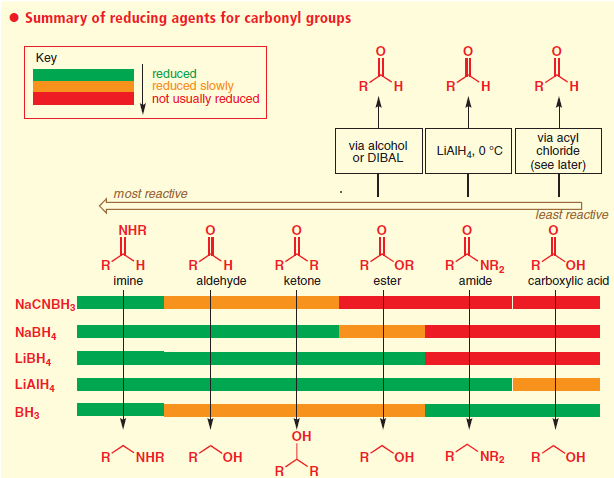
Ref: Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S. Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Oxford UP: Oxford, U.K., 2012; p 534.
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
For review papers and other articles,
refer to the tab "References"
Mechanism
Borane Reduction – General Mechanism
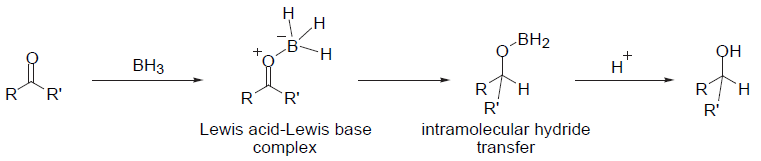
Additional details
General Procedure:
To a solution of acid or amide (1 eq.) in dry THF (10 Vol) at 0 oC is added BH3.THF or BH3.Me2S (1 eq.) dropwise for 1 h. It was brought to room temperature and stirred for 8 h. The reaction is monitored by TLC. (If the reaction does not proceed, it shall be heated to 40 to 50 oC) . After the completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture is cooled to 0 C and quenched by adding methanol or ethanol (Note: effervescence is observed). After stirring at room temperature for 2 h, the reaction mixture is poured into water (10 Vol) and extracted with DCM or EtOAc. The organic layer is then successively washed with water (10 Vol) and brine solution, dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to get the desired compound. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- The borane-dimethylsulfide (BMS) complex exhibits improved stability and solubility compared to the borane-THF complex. Both BMS and BH3.THF are used on manufacturing scale
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
- Amide to amine by BH3.THF (OrgSyn) — Open access
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
WO2010045258, page No. 127 (Acid to Alcohol)

WO2007121484, page No. 95 (Acid to Alcohol)
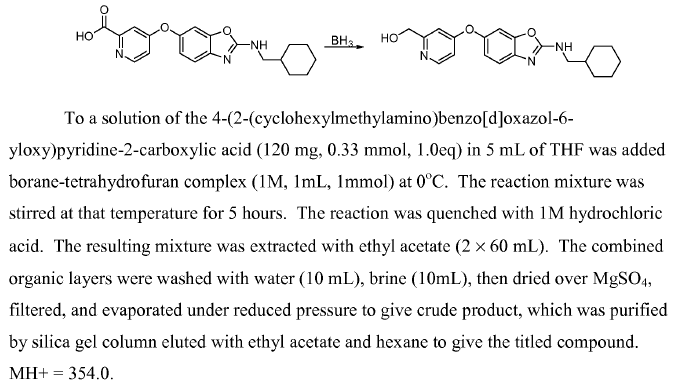

WO2007128568, page No. 82 (Amide to amine)

Green Chem
Borane reductions using BH3.THF or BH3.Me2S have been carried out on large-scale and there are several reports available in OPRD
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
- Chemical Development of an α2δ Ligand, (3S,5R)-3-(Aminomethyl)-5-methyloctanoic Acid (OPRD, 2011) – 842.7 Kg batch (acid) and 101 Kg BH3.Me2S complex are used — Carboxylic acid reduction to primary alcohol

- Initial Process Development and Scale-Up of the Synthesis of a Triple Reuptake Inhibitor ALB 109780 (OPRD, 2012) – 565 g batch (amide); 300 mL BH3.Me2S complex are used — Amide reduction to Amine
- Process Development and Scale-Up of a Benzoxazepine-Containing Kinase Inhibitor (OPRD, 2015) – 19.8 Kg batch; 288 Kg borane.THF complex are used — Amide reduction to Amine
- Kilogram Synthesis of a Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (OPRD, 2008) – 6.2 Kg batch; 12.9 Kg borane·THF (1M in THF) — Carboxylic acid reduction to primary alcohol
Green Chemistry Aspects:
Useful articles for Scale-up:
Borane reductions – Reviews :



