& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
- Heck coupling: C-C bond formation involving alkene and organohalide to generate substituted alkene
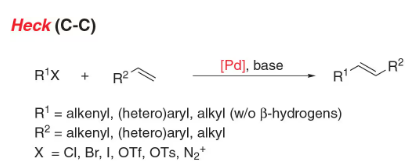
- Reactant-1 (Nucleophile): Alkene
- Reactant-2 (Electrophile): Organohalide [Aryl, Benzyl, Alkenyl, or Alkyl (with no β Hydrogens)]
- Solvents: DMF
- Catalyst: Catalytic Palladium [Pd(PPh3)4 (tetrakis), (Ph3P)2PdCl2 (dikis)]
- Bases: KOAc, NaOAc, NaHCO3, 2° or 3° amine
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
- Heck Coupling (SynArchive) – Excellent compilation of reaction schemes with references
Mechanism
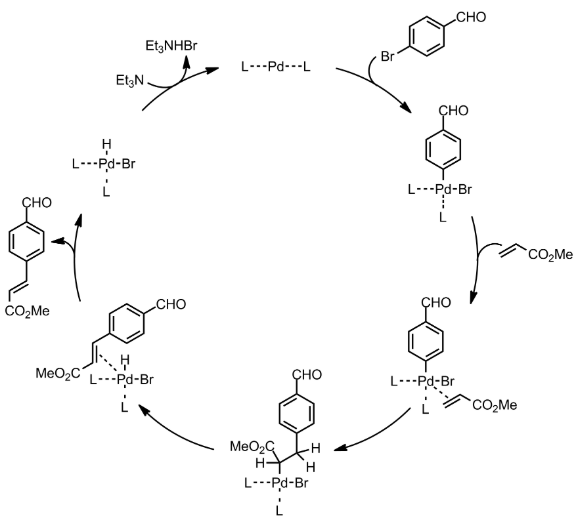
Heck Coupling – General Mechanism
- With the exception of the Heck reaction, all of the coupling reactions (Suzuki, Buchwald, Stille, Sonogashira and Negishi) follow the same general catalytic cycle: 1) oxidative addition of the organic halide; 2) ligand substitution of the nucleophile for the halide and 3) reductive elimination of the new organic product.
- The Heck reaction follows a similar mechanism involves: 1) oxidative addition; 2) ligand substitution by the alkene; 3) migratory insertion; 4) ß-hydride elimination and 5) reductive elimination
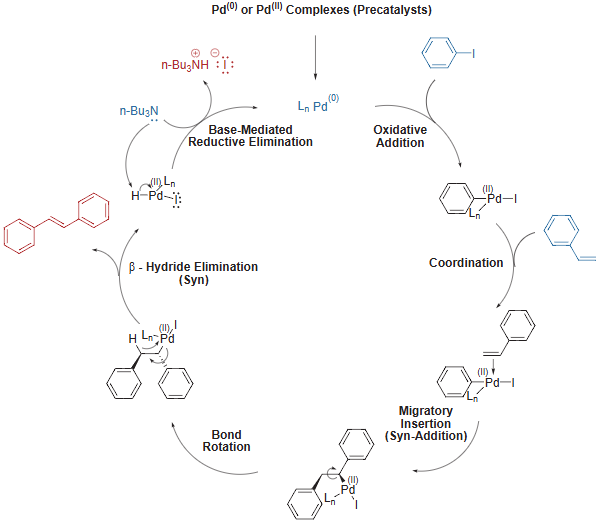
Heck Coupling – Mechanism with specific example
Additional details

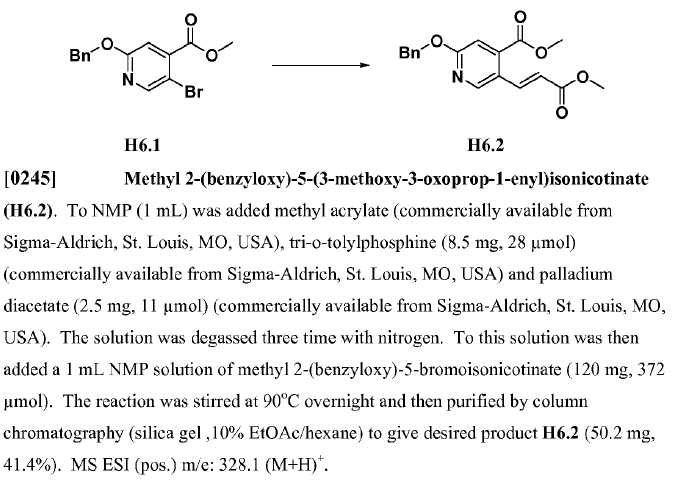
General Procedure:
Bromo-aromatic ring (1 equiv.), methyl acrylate (5 equiv.), TEA (1.5 equiv.), catalyst Pd(OAc)2 (0.1 equiv.), and P(o-Tolyl)3 (0.1 equiv.) were mixed in acetonitrile (depends on the scale). The mixture was degassed and heated to reflux for 5 hours under nitrogen atmosphere. The resulting mixture was filtered with celite and the filtrate was concentrated. The resultant residue was purified by silica gel column to give rise to the desired compound.
Note:
- The reaction conditions tolerate a wide range of functional groups on the olefin (Esters, ethers, carboxylic acids, nitriles, phenols, dienes are well tolerated on the olefin component. However, allylic alcohols tend to undergo rearrangement)
- Heck Coupling is stereospecific. Both the migratory insertion and the hydride elimination proceed with syn stereochemistry.
- Aryl chlorides are not good substrates, as they tend to react slowly, resulting in lower yields.
- Substrates with beta-hydrogen atoms undergoes beta-elimination, leading to olefin formation
- When the olefin substrate is more substituted, the reaction proceeds slower
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
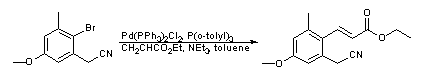
- High temperature Heck coupling of (2-bromo-5-methoxy-3-methylphenyl)-acetonitrile with ethyl acrylate (ChemSpider) — Open access
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
WO2010045258, page no. 92
Green Chem
Heck coupling has been carried out on large-scale.
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
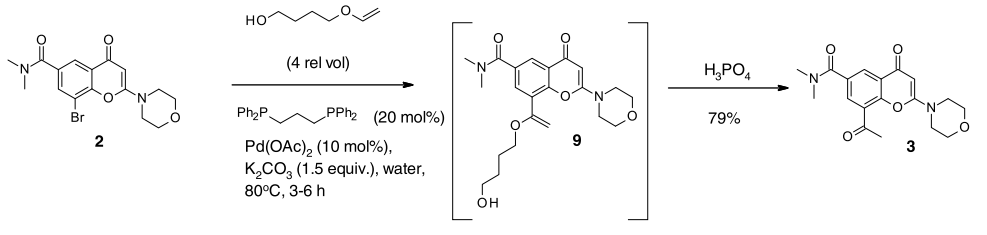
- Development and Scale-Up of an Asymmetric Synthesis of AZD8186 Using the Fukuyama Modification of the Mitsunobu Reaction (OPRD, 2021) – 5.5 Kg batch (Bromo derivative), Pd(OAc)2 (323 g) and Ligand (bis-(1,3-diphenylphosphino)propane, 1.19 Kg), hydroxybutyl vinyl ether (33.52 Kg) are used
Here, Stille coupling that was used in Medicinal chemistry route has been replaced by Heck coupling for Scale-up
Green Chemistry Aspects:
Heck Coupling – Reviews :