& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
- Hydrolysis of nitriles is carried out by heating either with dilute acid (e.g dil. HCl) or with an alkali (e.g: NaOH solution).
- In both condition, the reaction goes via two stages namely (a) nitrile to amide and (b) amide to carboxylic acid
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
For review papers and other articles,
refer to the tab "References"
Mechanism
Nitrile Hydrolysis – Mechanism
Additional details

General Procedure:
To a solution of nitrile (1 eq.) in MeOH or EtOH (10 Vol) is added 10% aq. NaOH or KOH (2 Vol) and stirred for 16 h The reaction is monitored by TLC. (If the reaction does not proceed, it shall be heated to 60 oC) . The reaction mixture is concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue diluted with water (10 Vol) and extracted with DCM (10 Vol x 2). The aqueous layer is cooled, acidified to pH 3 using 1 N HCl and extracted with DCM (2 x 5 Vol). The combined organic layer is then successively washed with water (10 Vol) and brine solution, dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to get the desired compound. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
Note:
- The solvent is EtOH or MeOH, along with water
- Most common bases are KOH and NaOH. Even LiOH could be used.
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
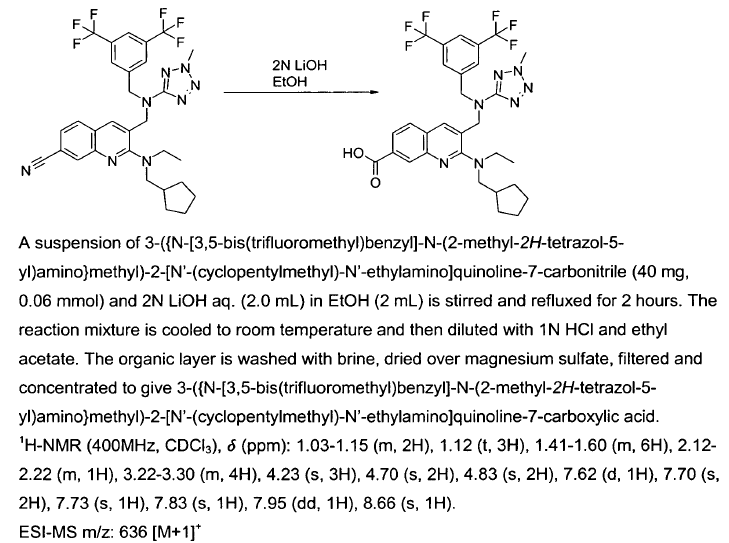
WO2007128568, page No. 52
Green Chem
Hydrolysis of Nitriles could easily be performed manufacturing scale.
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
Hydrolysis of Nitriles using acidic or basic condition have been performed on manufacturing scale.
Scale-Up Typical Procedure: