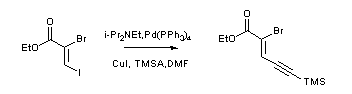& Mechanism
Green Chem
& Mechanism
Reaction & Reagents info
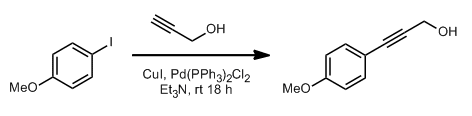
- Sonogashira coupling: C-C bond formation involving aryl or vinyl halides with terminal alkynes to generate conjugated enynes and arylalkynes.
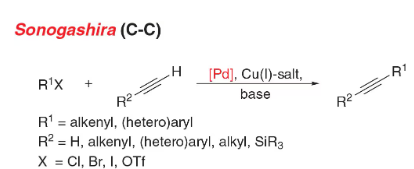
- Reactant-1 (Nucleophile): Terminal Alkyne
- Reactant-2 (Electrophile): Organohalide
- Solvents: THF, CH3CN, EtOAc
- Catalyst: Catalytic Palladium [Pd(PPh3)4 (tetrakis), (Ph3P)2PdCl2 (dikis)] & Cu(I) salt [CuI or CuBr]
- Bases: Et3N
Useful Links on Reagent & Reaction:
- Sonogashira Coupling (SynArchive) – Excellent compilation of reaction schemes with references
Mechanism
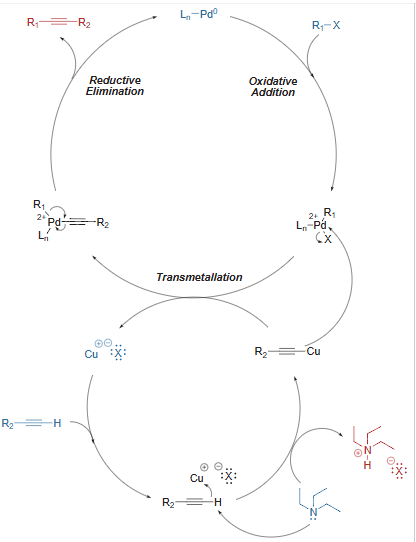
Sonogashira Coupling – General Mechanism
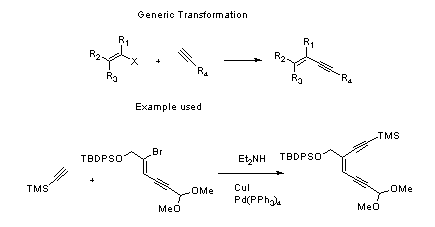
- The mechanism follows Oxidative addition – Reductive elimination cycle.
- Palladium and copper co-catalyzed Sonogashira coupling is reported to proceed via two independent catalytic cycles
Sonogashira Coupling – Mechanism with specific example
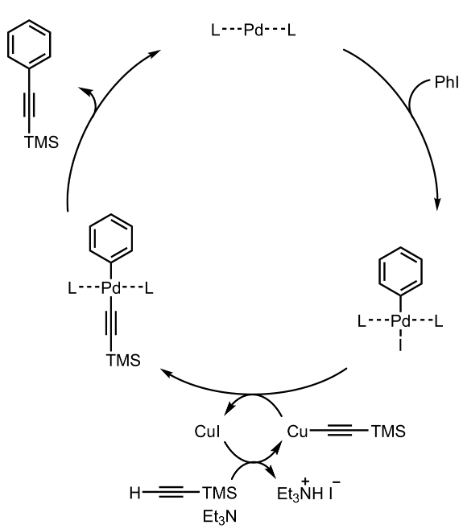
Additional details
General Procedure:
A mixture of Bromo-aromatic ring (1 eq ), alkyne derivative (1 eq), bis(triphenyl phosphine)palladium [II]cholride (0.025eq ) and CuI (0.1eq ) were taken in freshly distilled DIPEA (10 Vol). The mixture degassed, and stirred at room tempperature overnight under nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction was quenched with aq. NH4Cl (10 Vol, 10% solution) and extracted with EtOAc. The solvent was distilled off and the resultant residue was purified by silica gel column to get the desired compound.
Note:
- This reaction is highly stereospecific and regioselective, as similar to Suzuki.
- The general trend of substrate reactivity towards oxidative addition:
vinyl iodide ≥ vinyl triflate > vinyl bromide > vinyl chloride > aryl iodide > aryl triflate ≥ aryl bromide >> aryl chloride
- The terminal alkyne substrate exhibits a relatively broad range of functional group compatibility
For more details on reactions and reagents,
refer to the tab "Reaction, Reagents and Mechanism"
Typical Procedure:
For more details on large-scale reactions and OPRD procedures,
refer to the tab "Scale-up & Green Chem"
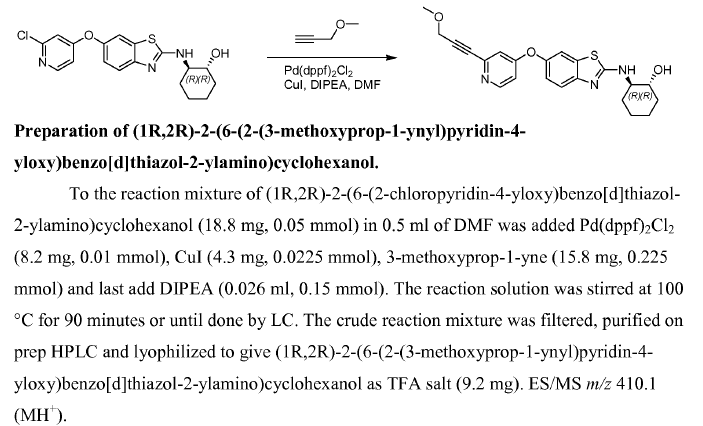
WO2007121484, page no. 174
Green Chem
Sonogashira coupling has been carried out on large-scale.
Scale-Up Typical Procedure:
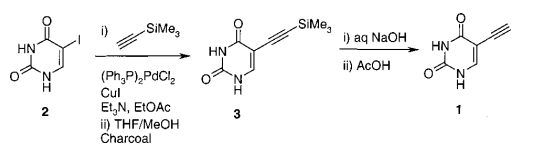
- Process Research and Development of a Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase Inactivator: Large-Scale Preparation of Eniluracil Using a Sonogashira Coupling (OPRD, 2001) – 64 Kg batch (I derivative); PdCl2(PPh3)2 (0.95 Kg) and CuI (0.26 Kg) are used
Green Chemistry Aspects: